Mitochondrial Dysfunction Associates With Acute T Lymphocytopenia and Impaired Functionality in COVID-19 Patients
- PMID: 35095881
- PMCID: PMC8795605
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.799896
Mitochondrial Dysfunction Associates With Acute T Lymphocytopenia and Impaired Functionality in COVID-19 Patients
Abstract
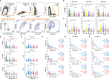
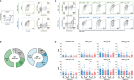
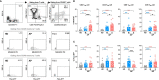
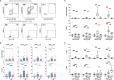
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection results in rapid T lymphocytopenia and functional impairment of T cells. The underlying mechanism, however, remains incompletely understood. In this study, we focused on characterizing the phenotype and kinetics of T-cell subsets with mitochondrial dysfunction (MD) by multicolor flow cytometry and investigating the association between MD and T-cell functionality. While 73.9% of study subjects displayed clinical lymphocytopenia upon hospital admission, a significant reduction of CD4 or CD8 T-cell frequency was found in all asymptomatic, symptomatic, and convalescent cases. CD4 and CD8 T cells with increased MD were found in both asymptomatic and symptomatic patients within the first week of symptom onset. Lower proportion of memory CD8 T cell with MD was found in severe patients than in mild ones at the stage of disease progression. Critically, the frequency of T cells with MD in symptomatic patients was preferentially associated with CD4 T-cell loss and CD8 T-cell hyperactivation, respectively. Patients bearing effector memory CD4 and CD8 T cells with the phenotype of high MD exhibited poorer T-cell responses upon either phorbol 12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA)/ionomycin or SARS-CoV-2 peptide stimulation than those with low MD. Our findings demonstrated an MD-associated mechanism underlying SARS-CoV-2-induced T lymphocytopenia and functional impairment during the acute phase of infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; T-cell functionality; memory T cell; mitochondrial dysfunction (MD).
Copyright © 2022 Mo, To, Zhou, Liu, Cao, Huang, Du, Lim, Yim, Luk, Chan, Chik, Lau, Tsang, Tam, Hung, Yuen and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard: World Health Organization (2021). Available at: https://covid19.who.int/ (Accessed updated June 15).
-
- Chan JF, Yuan S, Kok KH, To KK, Chu H, Yang J, et al. . A Familial Cluster of Pneumonia Associated With the 2019 Novel Coronavirus Indicating Person-to-Person Transmission: A Study of a Family Cluster. Lancet (Lond Engl) (2020) 395(10223):514–23. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30154-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

