Identification of Robust Biomarkers for Early Predicting Efficacy of Subcutaneous Immunotherapy in Children With House Dust Mite-Induced Allergic Rhinitis by Multiple Cytokine Profiling
- PMID: 35095890
- PMCID: PMC8789884
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.805404
Identification of Robust Biomarkers for Early Predicting Efficacy of Subcutaneous Immunotherapy in Children With House Dust Mite-Induced Allergic Rhinitis by Multiple Cytokine Profiling
Abstract
Background: Subcutaneous immunotherapy (SCIT) is an effective treatment for children with allergic rhinitis (AR), but its efficacy fluctuates among patients. There are no reliable candidate biomarkers for monitoring and predicting the response to SCIT. The present study aims to identify novel biomarkers for early predicting the efficacy of SCIT in pediatric AR patients based on multiple cytokine profiling.
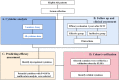
Methods: We prospectively recruited 72 children with house dust mite (HDM)-induced AR who were assigned to receive SCIT. The serum samples were collected and multiple cytokine profiling was conducted by Luminex assay at baseline. All patients were followed-up for 1 year and then categorized into effective and ineffective group based on their efficacy, and levels of 48 selected cytokines were tested and compared between the two groups. The potential cytokines were further validated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) in a cohort with 54 responders and 26 non-responders.
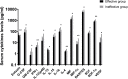
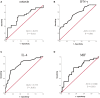
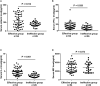
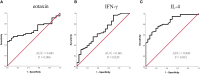
Results: Sixty-nine of 72 children completed one-year follow-up schedule with 46 included in effective group and 23 in ineffective group. The results of multiple cytokine profiling showed that 15 cytokines (eotaxin, G-CSF, GM-CSF, IFN-γ, IL-12(p40), IL-13, IL-15, IL-16, IL-4, MIF, MIP-1α, RANTES, SCF, SDF-1α and VEGF) were dysregulated between effective and ineffective group (all P < 0.05). Unadjusted and adjusted multivariate analysis models highlighted that serum eotaxin, IFN-γ, IL-4 and MIF levels closely associated with the efficacy of SCIT in pediatric HDM-induced AR patients. In addition, receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves revealed potential values of these four biomarkers in predicting the response to SCIT. Further ELISA validation results in the cohort of 80 pediatric patients demonstrated that serum eotaxin and IL-4 levels were elevated in responders while IFN-γ levels decreased in responders (all P < 0.05). ROC curves demonstrated that serum IL-4 exhibited more reliable accuracy in predicting SCIT efficacy than eotaxin and IFN-γ.
Conclusion: Our discover-validation study suggested that cytokines including IL-4, eotaxin and IFN- γ may serve as robust biomarkers for early predicting response of SCIT in children with HDM-induced AR. These results strengthen the evidence that cytokines were associated with the response of SCIT and contributed to understand its underlying therapeutic mechanisms.
Keywords: allergic rhinitis; biomarker; children; cytokine; subcutaneous immunotherapy.
Copyright © 2022 Xie, Fan, Tang, Cai, Zhang, Wang, Xie, Gao, Zhang, Xie and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dust mite component Analysis: Identifying key allergens components for effective immunotherapy in allergic rhinitis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Dec;125(Pt A):111111. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.111111. Epub 2023 Nov 4. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37925948
-
Immune signatures predict response to house dust mite subcutaneous immunotherapy in patients with allergic rhinitis.Allergy. 2024 May;79(5):1230-1241. doi: 10.1111/all.16068. Epub 2024 Feb 25. Allergy. 2024. PMID: 38403941
-
Augmented type 2 inflammatory response in allergic rhinitis patients experiencing systemic reactions to house dust mite subcutaneous immunotherapy.Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2024 Aug;35(8):e14207. doi: 10.1111/pai.14207. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39092594
-
An evidence-based analysis of house dust mite allergen immunotherapy: a call for more rigorous clinical studies.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013 Dec;132(6):1322-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.09.004. Epub 2013 Oct 18. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24139829 Review.
-
House Dust Mite Sublingual Immunotherapy for Pediatric Patients With Allergic Asthma.Ann Pharmacother. 2018 Oct;52(10):1019-1030. doi: 10.1177/1060028018769443. Epub 2018 Apr 11. Ann Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29642713 Review.
Cited by
-
Biomarkers in allergen immunotherapy: Focus on eosinophilic inflammation.Asia Pac Allergy. 2024 Mar;14(1):32-38. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.0000000000000129. Epub 2023 Dec 18. Asia Pac Allergy. 2024. PMID: 38482456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms and biomarkers of successful allergen-specific immunotherapy.Asia Pac Allergy. 2022 Oct 31;12(4):e45. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2022.12.e45. eCollection 2022 Oct. Asia Pac Allergy. 2022. PMID: 36452016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent developments in immunotherapy approaches for allergic rhinitis.World J Clin Cases. 2024 Nov 6;12(31):6451-6461. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i31.6451. World J Clin Cases. 2024. PMID: 39507117 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Focused allergic rhinitis practice parameter for Canada.Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2024 Aug 8;20(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13223-024-00899-3. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39118164 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes Derived hsa-miR-4669 as a Novel Biomarker for Early Predicting the Response of Subcutaneous Immunotherapy in Pediatric Allergic Rhinitis.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Sep 3;15:5063-5074. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S379414. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 36091336 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

