Breaking community boundary: Comparing academic and social communication preferences regarding global pandemics
- PMID: 35096139
- PMCID: PMC8787459
- DOI: 10.1016/j.joi.2021.101162
Breaking community boundary: Comparing academic and social communication preferences regarding global pandemics
Abstract
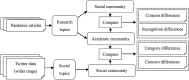
The global spread of COVID-19 has caused pandemics to be widely discussed. This is evident in the large number of scientific articles and the amount of user-generated content on social media. This paper aims to compare academic communication and social communication about the pandemic from the perspective of communication preference differences. It aims to provide information for the ongoing research on global pandemics, thereby eliminating knowledge barriers and information inequalities between the academic and the social communities. First, we collected the full text and the metadata of pandemic-related articles and Twitter data mentioning the articles. Second, we extracted and analyzed the topics and sentiment tendencies of the articles and related tweets. Finally, we conducted pandemic-related differential analysis on the academic community and the social community. We mined the resulting data to generate pandemic communication preferences (e.g., information needs, attitude tendencies) of researchers and the public, respectively. The research results from 50,338 articles and 927,266 corresponding tweets mentioning the articles revealed communication differences about global pandemics between the academic and the social communities regarding the consistency of research recognition and the preferences for particular research topics. The analysis of large-scale pandemic-related tweets also confirmed the communication preference differences between the two communities.
Keywords: Academic communication; COVID-19; Global pandemic; Sentiment analysis; Social communication; Topic mining.
© 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Aristovnik A., Ravelj D., Umek L. A bibliometric analysis of COVID-19 across science and social science research landscape. Sustainability. 2020;12(21):1–30. - PubMed
-
- Blei D.M., Ng A.Y., Jordan M.I. Latent dirichlet allocation. Journal of Machine Learning Research. 2003;3:993–1022.
-
- Bornmann L. Alternative metrics in scientometrics: A meta-analysis of research into three altmetrics. Scientometrics. 2015;103(3):1123–1144.
-
- Bruns A., Weller K., Zimmer M., Proferes N.J. A topology of Twitter research: Disciplines, methods, and ethics. ASLIB Journal of Information Management. 2014;66(3):250–261.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
