Role of GDNF, GFRα1 and GFAP in a Bifidobacterium-Intervention Induced Mouse Model of Intestinal Neuronal Dysplasia
- PMID: 35096711
- PMCID: PMC8796853
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2021.795678
Role of GDNF, GFRα1 and GFAP in a Bifidobacterium-Intervention Induced Mouse Model of Intestinal Neuronal Dysplasia
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effects of glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), GDNF family receptor alpha 1 (GFRα1), and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) on colonic motility in a mouse model of intestinal neuronal dysplasia by intervention with Bifidobacterium and to explore the influence of Bifidobacterium on enteric glial cells (EGCs).
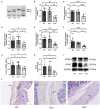
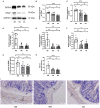
Methods: Western blotting and qRT-PCR were employed to detect the expression of GFRα1 and GFAP in colonic tissues of mice with or without Tlx2 mutations, and ELISA was used to detect the expression of GDNF in serum. IHC was used to detect the appearance of the ganglion cells. Subsequently, Tlx2 homozygous mutant (Tlx2-/-) mice were treated with Bifidobacterium. Colonic motility was measured before and after intervention by measuring the glass bead expelling time. The variations in abdominal circumference and GDNF, GFRα1, and GFAP expression were measured. In addition, 16SrRNA gene sequencing was performed to detect the abundance of the intestinal microbiota.
Results: The mRNA and protein expression of GFRα1 and GFAP was decreased in the colonic tissues of Tlx2-/- mice and GDNF expression was decreased in serum compared with Tlx2+/- and WT mice. After confirming the colonization of Bifidobacterium by 16S rRNA gene sequencing, the expelling time and abdominal distension were ameliorated, and the expression of GFAP, GDNF, and GFRα1 was increased.
Conclusions: The expression of GDNF, GFRα1, and GFAP is associated with colonic motility. The altered expression of EGC-related factors suggested that Bifidobacterium may be involved in the EGC activation process. The amelioration of IND symptoms after intervention with Bifidobacterium prompted the elicitation of adjuvant therapy.
Keywords: Bifidobacterium; GDNF; gut microbiota; homozygous mutant mice of Tlx2; intestinal neuronal dysplasia (IND).
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Zhou, Tian, Yu, Ren, Cao, Hou, Zhang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Toll-like receptor 2 regulates intestinal inflammation by controlling integrity of the enteric nervous system.Gastroenterology. 2013 Dec;145(6):1323-33. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.08.047. Epub 2013 Aug 28. Gastroenterology. 2013. PMID: 23994200
-
Effect of Neuroligin1 and Neurexin1 on the Colonic Motility in a Mouse Model of Neuronal Intestinal Dysplasia.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2020 Jan 4;2020:9818652. doi: 10.1155/2020/9818652. eCollection 2020. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 32184818 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Rafts Are Physiologic Membrane Microdomains Necessary for the Morphogenic and Developmental Functions of Glial Cell Line-Derived Neurotrophic Factor In Vivo.J Neurosci. 2015 Sep 23;35(38):13233-43. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2935-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26400951 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution of enteric glia and GDNF during gut inflammation.BMC Gastroenterol. 2011 Jan 14;11:3. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-11-3. BMC Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21235736 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of gestational inflammation on age-related cognitive decline and hippocampal Gdnf-GFRα1 levels in F1 and F2 generations of CD-1 Mice.BMC Neurosci. 2023 Apr 13;24(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s12868-023-00793-5. BMC Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37055728 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Enteric glia as a player of gut-brain interactions during Parkinson's disease.Front Neurosci. 2023 Nov 1;17:1281710. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1281710. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38027511 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Meier-Ruge W. [Casuistic of colon disorder with symptoms of Hirschsprung's disease (author's transl)]. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol. (1971) 55:506–10. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

