New Aspects of Kidney Fibrosis-From Mechanisms of Injury to Modulation of Disease
- PMID: 35096904
- PMCID: PMC8790098
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2021.814497
New Aspects of Kidney Fibrosis-From Mechanisms of Injury to Modulation of Disease
Abstract
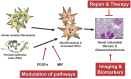
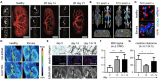
Organ fibrogenesis is characterized by a common pathophysiological final pathway independent of the underlying progressive disease of the respective organ. This makes it particularly suitable as a therapeutic target. The Transregional Collaborative Research Center "Organ Fibrosis: From Mechanisms of Injury to Modulation of Disease" (referred to as SFB/TRR57) was hosted from 2009 to 2021 by the Medical Faculties of RWTH Aachen University and the University of Bonn. This consortium had the ultimate goal of discovering new common but also different fibrosis pathways in the liver and kidneys. It finally successfully identified new mechanisms and established novel therapeutic approaches to interfere with hepatic and renal fibrosis. This review covers the consortium's key kidney-related findings, where three overarching questions were addressed: (i) What are new relevant mechanisms and signaling pathways triggering renal fibrosis? (ii) What are new immunological mechanisms, cells and molecules that contribute to renal fibrosis?, and finally (iii) How can renal fibrosis be modulated?
Keywords: crystals; deep learning; fibrosis imaging; inflammasome; lupus erythematodes; myofibroblast; parietal epithelial cell; renal fibrosis.
Copyright © 2022 Moeller, Kramann, Lammers, Hoppe, Latz, Ludwig-Portugall, Boor, Floege, Kurts, Weiskirchen and Ostendorf.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

