Resveratrol Ameliorates Intestinal Damage Challenged With Deoxynivalenol Through Mitophagy in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 35097052
- PMCID: PMC8793063
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2021.807301
Resveratrol Ameliorates Intestinal Damage Challenged With Deoxynivalenol Through Mitophagy in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
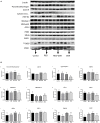
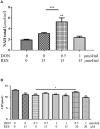
Deoxynivalenol (DON) reduces growth performance and damage intestinal function, and resveratrol (RES) has positive effects on growth performance and intestinal function. The purpose of this study was to investigate the protective mechanism of RES in vitro and vivo challenged with DON. The results showed that dietary supplementation with DON significantly increase the mRNA expression levels of mitophagy- related genes, and protein level for PINK1, Parkin, Beclin-1, Lamp, Atg5, Map1lc, Bnip3, Fundc1, Bcl2l1 and SQSTMS1 (P < 0.05), while supplementation with both RES and DON decreased those indexes in the ileum. Besides DON significantly decreased protein level for Pyruvate Dehydrogenase, Cytochrome c, MFN1, OPA1, and PHB1 (P < 0.05), while supplementation with both RES and DON increased protein level for PHB1, SDHA, and VDAC in the ileum. Moreover, in vitro, we found that DON significantly decreased mitochondrial respiration (P < 0.05), while RES + DON increased the rate of spare respiratory capacity. Also, DON significantly decreased total NAD and ATP (P < 0.05), while RES + DON increased the total NAD and ATP. These results indicate that RES may ameliorates the intestinal damage challenged with deoxynivalenol through mitophagy in weaning piglets.
Keywords: deoxynivalenol; intestinal function; mitophagy; piglets; resveratrol.
Copyright © 2022 Huang, Zheng, Song, Wang, Xiao and Jiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

