Occupational fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonia in a halogen dishes manufacturer: A case report
- PMID: 35097102
- PMCID: PMC8771394
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i2.741
Occupational fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonia in a halogen dishes manufacturer: A case report
Abstract
Background: Fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (FHP) is an allergic and diffuse pneumonia caused by repeated inhalation of antigenic substances, and sometimes developed in people working in specific environments. While novel antigens and exposures continued to be described, physicians should maintain a high suspicion of potential exposures. A detailed assessment of the patient's occupational exposures as well as living environment is necessary and complete allergen avoidance is the first and most important step in the management of FHP once the allergens are determined.
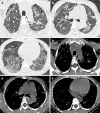
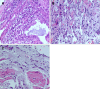
Case summary: A 35-year-old female was admitted to the hospital with a cough and breathing difficulties for more than one year. She was a nonsmoker and a manufacturer of halogen dishes, which are characteristic Chinese foods, for 15 years without any protection. High resolution computed tomography of the chest demonstrated an interstitial pneumonia pattern. Pulmonary function examination showed restricted ventilation dysfunction and a significant reduction in dispersion ability. Cell differentiation in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid demonstrated lymphocytosis (70.4%) with an increased lymphocyte CD4/CD8 ratio (0.94). Transbronchial lung biopsy combined with lung puncture pathology showed diffuse uniform alveolar interval thickening, chronic inflammatory cell infiltration, a proliferation of tissue in the bronchial wall fiber and alveolar epithelial follicle degeneration, resulting in fibrosis.
Conclusion: Exposure to spices used for the production of halogen dishes may cause FHP.
Keywords: Case report; Fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis; Halogen dishes; Inhalation; Interstitial pneumonia; Spices.
©The Author(s) 2022. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest related to this report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fibrotic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Diagnosed by a Re-evaluation with Bronchoalveolar Lavage at Disease Deterioration.Intern Med. 2023 Feb 15;62(4):577-582. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.9736-22. Epub 2022 Jul 22. Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 35871594 Free PMC article.
-
Bird fancier's lung: a series of 86 patients.Medicine (Baltimore). 2008 Mar;87(2):110-130. doi: 10.1097/MD.0b013e31816d1dda. Medicine (Baltimore). 2008. PMID: 18344808
-
[Hypersensitivity pneumonitis caused by Lyophyllum aggregatum in two sisters].Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2000 Aug;38(8):599-604. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2000. PMID: 11061085 Japanese.
-
Pathology of hypersensitivity pneumonitis.Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2008 Sep;14(5):440-54. doi: 10.1097/MCP.0b013e3283043dfa. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2008. PMID: 18664975 Review.
-
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: a noninfectious granulomatosis.Semin Respir Infect. 1995 Jun;10(2):96-106. Semin Respir Infect. 1995. PMID: 7569404 Review.
References
-
- Fernández Pérez ER, Crooks JL, Swigris JJ, Solomon JJ, Mohning MP, Huie TJ, Koslow M, Lynch DA, Groshong SD, Fier K. Design and rationale of a randomised, double-blind trial of the efficacy and safety of pirfenidone in patients with fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. ERJ Open Res. 2021;7 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chauvin P, Kerjouan M, Jégo P, Jouneau S, Lescoat A. [Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis: An update] Rev Med Interne. 2021;42:772–780. - PubMed
-
- D'Ippolito R, Chetta A, Foresi A, Marangio E, Castagnaro A, Merliniaft S, Zompatori M, Olivieri D. Induced sputum and bronchoalveolar lavage from patients with hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Respir Med. 2004;98:977–983. - PubMed
-
- Meyer KC, Raghu G. Reply: The clinical utility of bronchoalveolar lavage cellular analysis in interstitial lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013;187:777–778. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

