Unintended Pregnancy and Associated Factors among Women Who Live in Ilu Gelan District, Western Ethiopia, 2021
- PMID: 35097105
- PMCID: PMC8799332
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8646724
Unintended Pregnancy and Associated Factors among Women Who Live in Ilu Gelan District, Western Ethiopia, 2021
Abstract
Background: The World Health Organization Report noted that unintended pregnancy is the most common cause of maternal mortality in developing countries. Most unintended pregnancies occur where access to maternal care is limited, and because of this, many mothers lose their life. Therefore, this study was an attempt to assess the proportion of unintended pregnancy and associated factors among women who live in Ilu Gelan District, Western Ethiopia, 2021.
Method: A community-based cross-sectional study was conducted in the rural and urban kebeles of Ilu Gelan Woreda West Shoa Zone, Ethiopia, from March 1 to 30, 2021. The study population consists of 540 pregnant women who were living in Ilu Gelan Woreda for at least the last six months during the data collection period. Simple random sampling by lottery method was used to recruit the study subject. Data were checked, coded, entered to EpiData version 3, and then exported to SPSS version 25 for analysis. Both descriptive and analytical statistical procedures were utilized. Both bivariable and multivariable logistic regressions was implemented.
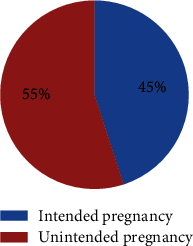
Result: In this study, the proportion of unintended pregnancy was found to be 55%, at 95% CI: 50.7-59.3. Multivariable logistic regression results showed that married women (AOR = 0.117, CI: 0.04-0.38), monthly income less than 1000 Ethiopian Birr (AOR = 4.93, CI: 1.72-14.09), gravidity greater than or equal to five (AOR = 6.07, CI: 2.4-15.28), birth interval less than 2 years (AOR = 3.35 (1.44-7.8)), lack of awareness about contraceptive (AOR = 2.06 (1.03-4.15)), and husband decision-making on health care (AOR = 11.1 (2.07-59.51)) were significantly associated with unintended pregnancy. Conclusion and Recommendation. This study indicated that more than half of pregnant women reported that their current pregnancy was found to be unintended pregnancy. Married women, family monthly income less than 1000 Ethiopian Birr, gravidity greater than or equal to five, birth space less than two years, lack of contraceptive awareness, and health care decisions by husband only showed a significant association with unintended pregnancy. To decrease the current level of unintended pregnancy, all concerned stakeholders should emphatically consider those identified factors for intervention; specifically, Ilu Gelan District Health Bureau and health providers should empower women with health education about family planning and decision-making related to their health issues in the study area.
Copyright © 2022 Ephrem Yohannes and Bikila Balis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Unintended pregnancy and the factors among currently pregnant married youths in Western Oromia, Ethiopia: A mixed method.PLoS One. 2021 Nov 4;16(11):e0259262. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259262. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34735534 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of unintended pregnancy and associated factors among married women in west Belessa Woreda, Northwest Ethiopia, 2016.Reprod Health. 2018 Dec 7;15(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s12978-018-0649-6. Reprod Health. 2018. PMID: 30526615 Free PMC article.
-
Respectful maternity care during facility-based child birth and associated factors in public health facilities of Ilu AbaBor zone, Southwest Ethiopia.Reprod Health. 2022 Apr 22;19(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s12978-022-01368-z. Reprod Health. 2022. PMID: 35459182 Free PMC article.
-
Magnitude, determinants, and adverse outcomes of unintended pregnancy among pregnant mothers in low- and middle-income countries: An umbrella review of systematic review and meta-analysis.J Glob Health. 2024 Dec 13;14:04253. doi: 10.7189/jogh.14.04253. J Glob Health. 2024. PMID: 39670318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unintended pregnancy and contraceptive use among women in low- and middle-income countries: systematic review and meta-analysis.Contracept Reprod Med. 2023 Nov 23;8(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s40834-023-00255-7. Contracept Reprod Med. 2023. PMID: 37993927 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Decision-making pathways for contraceptive use among refugee and host populations in Adjumani district, Uganda; an exploratory study.BMC Womens Health. 2024 Jul 26;24(1):427. doi: 10.1186/s12905-024-03272-z. BMC Womens Health. 2024. PMID: 39061042 Free PMC article.
-
Long-acting reversible and permanent contraceptives utilization and its associated factors among married women who desire no more children in Ethiopia: A multilevel analysis.PLoS One. 2025 Jan 24;20(1):e0316799. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0316799. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 39854289 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and determinants of unintended pregnancy among rural reproductive age women in Ethiopia.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 5;15(1):860. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-81067-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39757221 Free PMC article.
-
Unintended pregnancy and associated factors during COVID-19 pandemic in Ethiopia: Community-based cross-sectional study.Womens Health (Lond). 2022 Jan-Dec;18:17455057221118170. doi: 10.1177/17455057221118170. Womens Health (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35972047 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the Trends and Factors Associated With Unintended Pregnancy Among Women of Reproductive Age: An Analysis of the Nigerian Demographic Health Survey Between 2008 to 2018.Int J Sex Health. 2024 May 20;36(3):302-316. doi: 10.1080/19317611.2024.2346144. eCollection 2024. Int J Sex Health. 2024. PMID: 39148920 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barker G., Ricardo C., Nascimento M. Engaging men in changing gender based inequality in health: evidence from programme intervention . Geneva: World Health Organization; 2007.
-
- Brady M. Preventing sexually transmitted infections and unintended pregnancy, and safeguarding fertility: triple protection needs of young women. Reproductive Health Matters . 2003;11(22):134–141. - PubMed
-
- Pallitto C. C., García-Moreno C., Jansen H. A., Heise L., Ellsberg M., Watts C. Intimate partner violence, abortion, and unintended pregnancy: results from the WHO Multi-country Study on Women's Health and Domestic Violence. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics . 2013;120(1):3–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijgo.2012.07.003. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources