Switching from Insulin Degludec plus Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor to Insulin Degludec/Liraglutide Improves Glycemic Variability in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Preliminary Prospective Observation Study
- PMID: 35097130
- PMCID: PMC8793345
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5603864
Switching from Insulin Degludec plus Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor to Insulin Degludec/Liraglutide Improves Glycemic Variability in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Preliminary Prospective Observation Study
Abstract
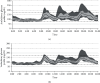
Incretins reduce glycemic variability (GV) in patients with type 2 diabetes, but it is unknown whether switching from a combination of basal insulin and a DPP-4 inhibitor to insulin degludec/liraglutide (IDegLira) improves GV. We performed an exploratory prospective observational study to compare the effect of IDegLira and the combination on GV. We recruited hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes who had stable glycemic control with insulin degludec (≤16 units/day) and taking a DPP-4 inhibitor. GV was analyzed using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) before and after switching the medication to IDegLira. The principal endpoint was the change in mean amplitude of glycemic excursions (MAGE). Other indices of GV and CGM parameters were analyzed as the secondary endpoints. Fifteen participants were enrolled and 12 completed the study. In these participants, the DPP-4 inhibitor and insulin degludec were discontinued, and the equivalent dose of IDegLira was commenced. Switching to IDegLira significantly improved MAGE from 74.9 (60.3, 97.7) mg/dL to 64.8 (52.0, 78.2) mg/dL (P < 0.05), as well as other indices of GV and 24-hour mean blood glucose concentration. Analysis of the ambulatory glucose profile showed marked reductions in postprandial glucose concentration. Nocturnal glucose concentration was similar under the two treatment regimens. IDegLira improved GV as well as the mean and the postprandial glucose concentration by switching from insulin degludec plus DPP-4 inhibitor combination. IDegLira might be beneficial for patients being treated with low-dose basal insulin.
Copyright © 2022 Yuki Oe et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AN has obtained research support from Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Taisho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. H.M. has received honoraria for lectures from Astellas Pharma Inc., Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Co., Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., MSD K.K., Novo Nordisk Pharma Ltd., Kowa Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Sanofi and has received research funding from Astellas Pharma Inc., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Co. Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Novo Nordisk Pharma, Kowa Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Abbott Japan Co., Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., LifeScan Japan Inc., and Taisho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. TA has received research grants from Astellas Pharma Inc., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co. Ltd., Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Pfizer Inc., Alexion Inc., Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and Teijin Pharma Ltd.; speaking fees from Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Astellas Pharma Inc., Takeda Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Pfizer Inc., AbbVie Inc., Eisai Co. Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd., Bristol-Myers Squibb Co., UCB Japan Co. Ltd., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Novartis Pharma K.K., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd., and Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.; and fees for consultancies from AstraZeneca plc., Medical & Biological Laboratories Co., Ltd., Pfizer Inc., AbbVie Inc., Ono Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd., Novartis Pharma K.K., and Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd. YO, HN, SK, YT, AY, RI, AM, and KYC have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A Fixed Ratio Combination of Insulin Degludec and Liraglutide (IDegLira) Reduces Glycemic Fluctuation and Brings More Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Within Blood Glucose Target Ranges.Diabetes Technol Ther. 2017 Apr;19(4):255-264. doi: 10.1089/dia.2016.0405. Epub 2017 Mar 10. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28282219 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
IDegLira Improves Both Fasting and Postprandial Glucose Control as Demonstrated Using Continuous Glucose Monitoring and a Standardized Meal Test.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2015 Oct 6;10(2):389-97. doi: 10.1177/1932296815610124. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2015. PMID: 26443290 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Insulin degludec/liraglutide (IDegLira) maintains glycaemic control and improves clinical outcomes, regardless of pre-trial insulin dose, in people with type 2 diabetes that is uncontrolled on basal insulin.Diabet Med. 2020 Feb;37(2):267-276. doi: 10.1111/dme.14178. Epub 2019 Nov 28. Diabet Med. 2020. PMID: 31705547 Free PMC article.
-
Role of incretin-based therapies and sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors as adjuncts to insulin therapy in Type 2 diabetes, with special reference to IDegLira.Diabet Med. 2016 Jul;33(7):864-76. doi: 10.1111/dme.13021. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Diabet Med. 2016. PMID: 26525806 Review.
-
Insulin degludec/liraglutide: innovation-driven combination for advancement in diabetes therapy.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2014 Jun;14(6):869-78. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2014.904851. Epub 2014 Apr 5. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24702171 Review.
Cited by
-
The Current and Future Role of Insulin Therapy in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes: A Narrative Review.Diabetes Ther. 2024 May;15(5):1085-1098. doi: 10.1007/s13300-024-01569-8. Epub 2024 Apr 4. Diabetes Ther. 2024. PMID: 38573469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of iGlarLixi on continuous glucose monitoring-measured time in range in insulin-naive adults with suboptimally controlled type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025 Apr;27(4):2173-2182. doi: 10.1111/dom.16214. Epub 2025 Feb 4. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025. PMID: 39905643 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Retrospective Study of IDegLira, a New Fixed-Ratio Combination, in Japanese Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Analysis of Background Factors Affecting Effectiveness After 6 Months of Treatment.J Clin Med Res. 2023 Sep;15(8-9):406-414. doi: 10.14740/jocmr4995. Epub 2023 Sep 30. J Clin Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37822852 Free PMC article.
-
What is Glycaemic Variability and which Pharmacological Treatment Options are Effective? A Narrative Review.touchREV Endocrinol. 2023 Jul;19(2):16-21. doi: 10.17925/EE.2023.19.2.4. Epub 2023 Jul 7. touchREV Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 38046184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety profile of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist in obese Type-2 diabetes patients from a private institution in Karachi.Pak J Med Sci. 2023 Jul-Aug;39(4):1113-1118. doi: 10.12669/pjms.39.4.7353. Pak J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37492314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nomoto H., Miyoshi H., Sugawara H., et al. A randomized controlled trial comparing the effects of dapagliflozin and DPP-4 inhibitors on glucose variability and metabolic parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus on insulin. Diabetology and Metabolic Syndrome . 2017;9(1):p. 54. doi: 10.1186/s13098-017-0255-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Miya A., Nakamura A., Cho K. Y., et al. Impact of endogenous insulin secretion on the improvement of glucose variability in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes treated with canagliflozin plus teneligliptin. Journal of Diabetes Investigation. . 2021;12(8):1395–1399. doi: 10.1111/jdi.13479. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

