A determination of pan-pathogen antimicrobials?
- PMID: 35098103
- PMCID: PMC8785259
- DOI: 10.1016/j.medidd.2022.100120
A determination of pan-pathogen antimicrobials?
Abstract
While antimicrobial drug development has historically mitigated infectious diseases that are known, COVID-19 revealed a dearth of 'in-advance' therapeutics suitable for infections by pathogens that have not yet emerged. Such drugs must exhibit a property that is antithetical to the classical paradigm of antimicrobial development: the ability to treat infections by any pathogen. Characterisation of such 'pan-pathogen' antimicrobials requires consolidation of drug repositioning studies, a new and growing field of drug discovery. In this review, a previously-established system for evaluating repositioning studies is used to highlight 4 therapeutics which exhibit pan-pathogen properties, namely azithromycin, ivermectin, niclosamide, and nitazoxanide. Recognition of the pan-pathogen nature of these antimicrobials is the cornerstone of a novel paradigm of antimicrobial development that is not only anticipatory of pandemics and bioterrorist attacks, but cognisant of conserved anti-infective mechanisms within the host-pathogen interactome which are only now beginning to emerge. Ultimately, the discovery of pan-pathogen antimicrobials is concomitantly the discovery of a new class of antivirals, and begets significant implications for pandemic preparedness research in a world after COVID-19.
Keywords: Bioterrorism; COVID-19; Drug repositioning; Host-pathogen interaction; Pan-pathogen antimicrobial; Pandemic.
Crown Copyright © 2022 Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
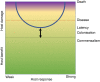
References
-
- Neu H.C., Gootz T.D. In: Medical microbiology. 4th ed. Baron S., editor. University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston; Galveston (TX): 1996. Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. Chapter 11.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
