Burden of hospitalization for heart failure in the United States: a systematic literature review
- PMID: 35098748
- PMCID: PMC10373049
- DOI: 10.18553/jmcp.2022.28.2.157
Burden of hospitalization for heart failure in the United States: a systematic literature review
Abstract
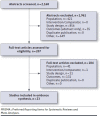
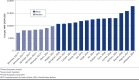
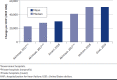
BACKGROUND: Heart failure (HF) affects approximately 6 million Americans, with prevalence projected to increase by 46% and direct medical costs to reach $53 billion by 2030. Hospitalizations are the largest component of direct costs for HF; however, recent syntheses of the economic and clinical burden of hospitalization for heart failure (HHF) are lacking. OBJECTIVE: To synthesize contemporary estimates of cost and clinical outcomes of HHF in the United States. METHODS: A systematic literature review was conducted using MEDLINE and Embase to identify articles reporting cost or charge per HHF in the United States published between January 2014 and May 2019. Subgroups of interest were those with both HF and renal disease or diabetes, as well as HF with reduced or preserved ejection fraction (HFrEF or HFpEF). RESULTS: 23 studies reporting cost and/or charge per HHF were included. Sample sizes ranged from 989 to approximately 11 million (weighted), mean age from 65 to 83 years, and 39% to 74% were male. Cost per HHF ranged from $7,094 to $9,769 (median) and $10,737 to $17,830 (mean). Charge per HHF ranged from $22,162 to $40,121 (median), and $50,569 to $50,952 (mean). Among patients with renal disease, HHF mean cost ranged from $9,922 to $41,538. For those with HFrEF or HFpEF, mean cost ranged from $11,600 to $17,779 and $7,860 to $10,551, respectively. No eligible studies were identified that reported HHF costs or charges among patients with HF and diabetes. Cost and charge per HHF increased with length of stay, which ranged from 3 to 5 days (median) and 4 to 7 days (mean). CONCLUSIONS: This synthesis demonstrates the substantial economic burden of HHF and the variability in estimates of this burden. Factors contributing to variability in estimates include length of stay, age and sex of the sample, HF severity, and frequencies of comorbidities. Further research into cost drivers of HHF is warranted to understand potential mechanisms to reduce associated costs. DISCLOSURES: This study was funded by Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals. Osenenko, Deighton, and Szabo are employees of Broadstreet HEOR, which received funds from Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals for this work. Kuti and Pimple are employees of Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals. This study was presented in abstract form at the 2020 American Heart Association (AHA) Quality of Care and Outcomes Research (QCOR) 2020 Scientific Sessions (May 15-16, Virtual Meeting).
Conflict of interest statement
This study was funded by Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals. Osenenko, Deighton, and Szabo are employees of Broadstreet HEOR, which received funds from Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals for this work. Kuti and Pimple are employees of Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals.
This study was presented in abstract form at the 2020 American Heart Association (AHA) Quality of Care and Outcomes Research (QCOR) 2020 Scientific Sessions (May 15-16, Virtual Meeting).
Figures
References
-
- Virani SS, Alonso A, Aparicio HJ, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2021 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;143(8):e254-e743. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous