Cu(I)-Catalyzed Alkynylation of Quinolones
- PMID: 35099185
- PMCID: PMC8845045
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.orglett.2c00020
Cu(I)-Catalyzed Alkynylation of Quinolones
Abstract
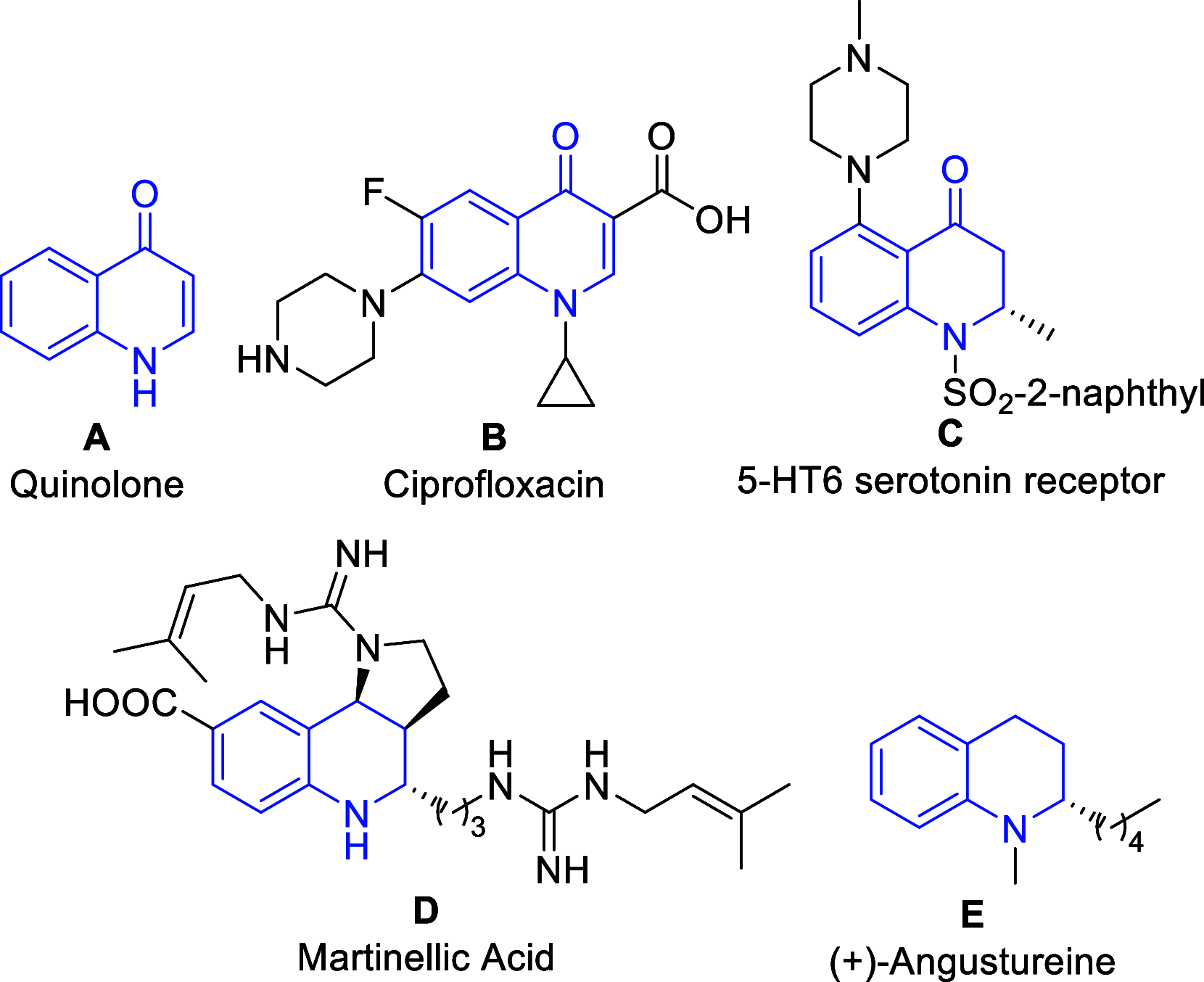
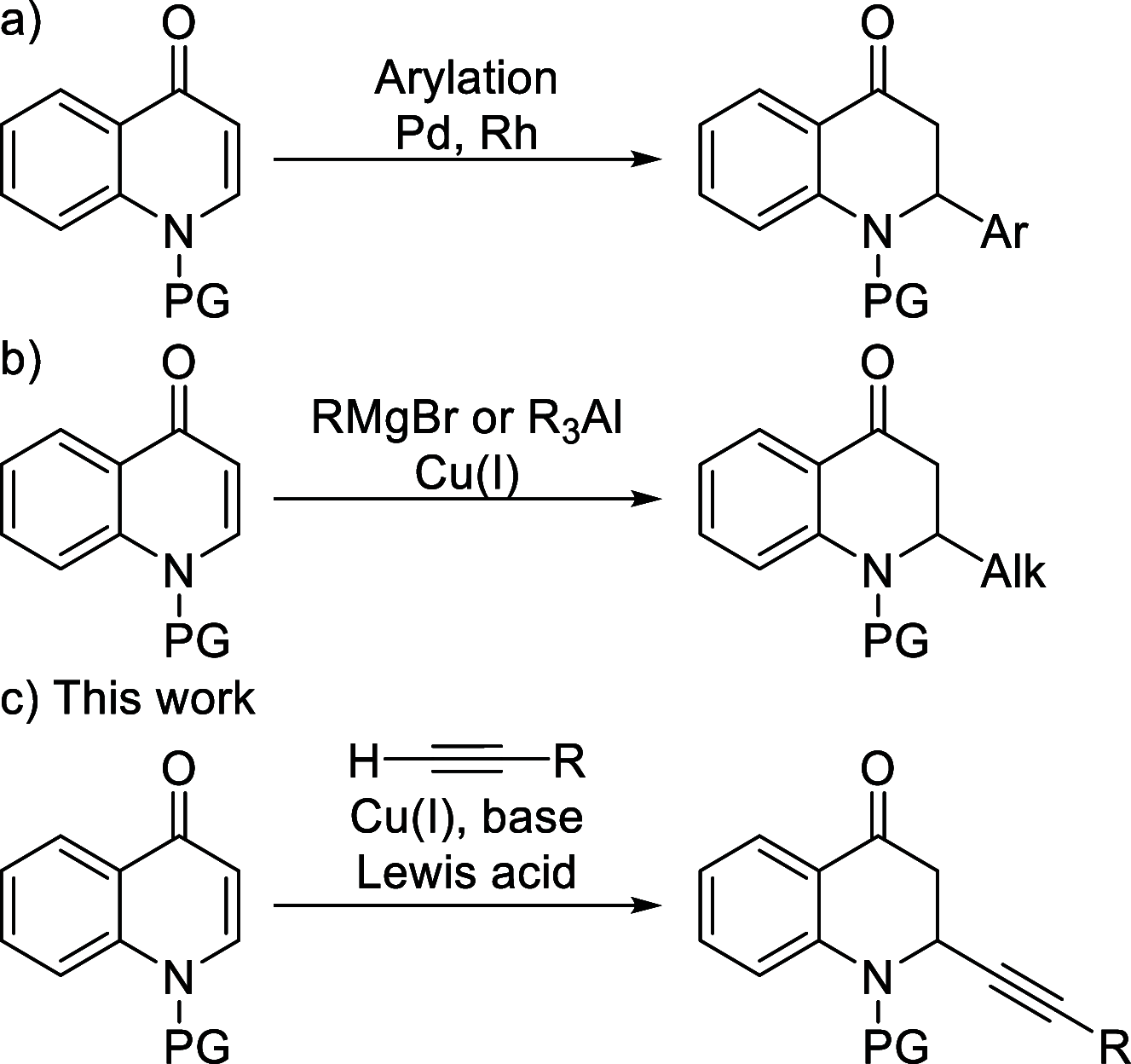
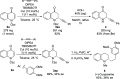
Herein we report the first alkynylation of quinolones with terminal alkynes under mild reaction conditions. The reaction is catalyzed by Cu(I) salts in the presence of a Lewis acid, which is essential for the reactivity of the system. The enantioselective version of this transformation has also been explored, and the methodology has been applied in the synthesis of the enantioenriched tetrahydroquinoline alkaloid cuspareine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Andriole V. T.The Quinolones: Prospects. In The Quinolones; Elsevier, 2000.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

