The anthropometric and physical qualities of women's rugby league Super League and international players; identifying differences in playing position and level
- PMID: 35100275
- PMCID: PMC8803183
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249803
The anthropometric and physical qualities of women's rugby league Super League and international players; identifying differences in playing position and level
Abstract
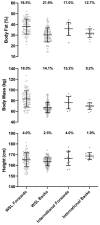
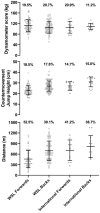
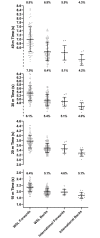
Participation in women's rugby league has been growing since the foundation of the English women's rugby league Super League in 2017. However, the evidence base to inform women's rugby league remains sparse. This study provides the largest quantification of anthropometric and physical qualities of women's rugby league players to date, identifying differences between positions (forwards & backs) and playing level (Women's Super League [WSL] vs. International). The height, weight, body composition, lower body strength, jump height, speed and aerobic capacity of 207 players were quantified during the pre-season period. Linear mixed models and effects sizes were used to determine differences between positions and levels. Forwards were significantly (p < 0.05) heavier (forwards: 82.5 ± 14.8kg; backs: 67.7 ± 9.2kg) and have a greater body fat % (forwards: 37.7 ± 6.9%; backs: 30.4 ± 6.3%) than backs. Backs had significantly greater lower body power measured via jump height (forwards: 23.5 ± 4.4cm; backs: 27.6 ± 4.9cm), speed over 10m (forwards: 2.12 ± 0.14s; backs: 1.98 ± 0.11s), 20m (forwards: 3.71 ± 0.27s; backs: 3.46 ± 0.20s), 30m (forwards: 5.29 ± 0.41s; backs: 4.90 ± 0.33s), 40m (forwards: 6.91 ± 0.61s; backs: 6.33 ± 0.46s) and aerobic capacity (forwards: 453.4 ± 258.8m; backs: 665.0 ± 298.2m) than forwards. Additionally, international players were found to have greater anthropometric and physical qualities in comparison to their WSL counterparts. This study adds to the limited evidence base surrounding the anthropometric and physical qualities of elite women's rugby league players. Comparative values for anthropometric and physical qualities are provided which practitioners may use to evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of players, informing training programs to prepare players for the demands of women's rugby league.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors would like to declare a commercial affiliation with the Rugby Football League. This affiliation does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comparison of fitness and skill among playing positions in sub-elite rugby league players.J Sci Med Sport. 2008 Nov;11(6):585-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jsams.2007.07.004. Epub 2007 Aug 27. J Sci Med Sport. 2008. PMID: 17720624
-
Longitudinal changes in anthropometric, physiological, and physical qualities of international women's rugby league players.PLoS One. 2024 May 14;19(5):e0298709. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298709. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38743656 Free PMC article.
-
Anthropometric and physical characteristics of english academy rugby league players.J Strength Cond Res. 2014 Feb;28(2):319-27. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0b013e3182a73c0e. J Strength Cond Res. 2014. PMID: 23942164
-
Match Demands, Anthropometric Characteristics, and Physical Qualities of Female Rugby Sevens Athletes: A Systematic Review.J Strength Cond Res. 2019 Dec;33(12):3463-3474. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000003339. J Strength Cond Res. 2019. PMID: 31453939
-
Anthropometric and Physiological Characteristics of Elite Male Rugby Athletes.J Strength Cond Res. 2020 Jun;34(6):1790-1801. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000002827. J Strength Cond Res. 2020. PMID: 30138238 Review.
Cited by
-
Longitudinal study of five seasons of upper limb injuries in training and matches in elite female rugby union at club and national team level.BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2025 Apr 3;11(2):e002359. doi: 10.1136/bmjsem-2024-002359. eCollection 2025. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2025. PMID: 40191841 Free PMC article.
-
Experiences of Female Rugby Union Players and Practitioners in Rehabilitation Following a Shoulder Injury.Sports (Basel). 2025 May 28;13(6):166. doi: 10.3390/sports13060166. Sports (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40559678 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of the physical characteristics of the French women's rugby players: A 10-year longitudinal analysis by position and team.Front Sports Act Living. 2023 Apr 5;5:1120162. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2023.1120162. eCollection 2023. Front Sports Act Living. 2023. PMID: 37090820 Free PMC article.
-
Validity, reliability, and the contributing physical characteristics of a modified 15m prone Yo-Yo Intermittent Recovery Test Level-1 test in elite female rugby league players.PLoS One. 2024 Jun 26;19(6):e0306171. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0306171. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38924067 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into breast health issues in women's rugby.Eur J Sport Sci. 2024 Dec;24(12):1735-1742. doi: 10.1002/ejsc.12128. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Eur J Sport Sci. 2024. PMID: 38952063 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rugby Football League. Women and Girls Rugby League: Player Pathway. 2019.

