Genetic analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans pry-1/Axin suppressors identifies genes involved in reproductive structure development, stress responses, and aging
- PMID: 35100345
- PMCID: PMC9210326
- DOI: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab430
Genetic analysis of Caenorhabditis elegans pry-1/Axin suppressors identifies genes involved in reproductive structure development, stress responses, and aging
Abstract
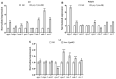
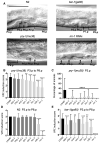
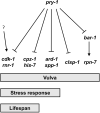
The Axin family of scaffolding proteins regulates a wide array of developmental and post-developmental processes in eukaryotes. Studies in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans have shown that the Axin homolog PRY-1 plays essential roles in multiple tissues. To understand the genetic network of pry-1, we focused on a set of genes that are differentially expressed in the pry-1-mutant transcriptome and are linked to reproductive structure development. Knocking down eight of the genes (spp-1, clsp-1, ard-1, rpn-7, cpz-1, his-7, cdk-1, and rnr-1) via RNA interference efficiently suppressed the multivulva phenotype of pry-1 mutants. In all cases, the ectopic induction of P3.p vulval precursor cell was also inhibited. The suppressor genes are members of known gene families in eukaryotes and perform essential functions. Our genetic interaction experiments revealed that in addition to their role in vulval development, these genes participate in one or more pry-1-mediated biological events. Whereas four of them (cpz-1, his-7, cdk-1, and rnr-1) function in both stress response and aging, two (spp-1 and ard-1) are specific to stress response. Altogether, these findings demonstrate the important role of pry-1 suppressors in regulating developmental and post-developmental processes in C. elegans. Given that the genes described in this study are conserved, future investigations of their interactions with Axin and their functional specificity promises to uncover the genetic network of Axin in metazoans.
Keywords: C. elegans; pry-1; Axin; WNT signaling; aging; stress response; vulva development.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Genetics Society of America.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Cabin1 domain-containing gene picd-1 interacts with pry-1/Axin to regulate multiple processes in Caenorhabditis elegans.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 14;12(1):12029. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15873-5. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35835800 Free PMC article.
-
Two functionally distinct Axin-like proteins regulate canonical Wnt signaling in C. elegans.Dev Biol. 2007 Aug 15;308(2):438-48. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.05.043. Epub 2007 Jun 6. Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17601533
-
Role of PRY-1/Axin in heterochronic miRNA-mediated seam cell development.BMC Dev Biol. 2019 Jul 15;19(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s12861-019-0197-5. BMC Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31307392 Free PMC article.
-
Axin Family of Scaffolding Proteins in Development: Lessons from C. elegans.J Dev Biol. 2019 Oct 15;7(4):20. doi: 10.3390/jdb7040020. J Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31618970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AXIN-AMPK signaling: Implications for healthy aging.F1000Res. 2021 Dec 8;10:1259. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.74220.1. eCollection 2021. F1000Res. 2021. PMID: 35087668 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The FGFR4 Homolog KIN-9 Regulates Lifespan and Stress Responses in Caenorhabditis elegans.Front Aging. 2022 May 20;3:866861. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2022.866861. eCollection 2022. Front Aging. 2022. PMID: 35821842 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amrit FRG, Ratnappan R, Keith SA, Ghazi A.. 2014. The C. elegans lifespan assay toolkit. Methods. 68:465–475. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
