spatzie: an R package for identifying significant transcription factor motif co-enrichment from enhancer-promoter interactions
- PMID: 35100401
- PMCID: PMC9122533
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkac036
spatzie: an R package for identifying significant transcription factor motif co-enrichment from enhancer-promoter interactions
Abstract
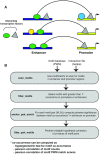
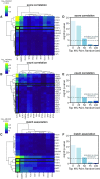
Genomic interactions provide important context to our understanding of the state of the genome. One question is whether specific transcription factor interactions give rise to genome organization. We introduce spatzie, an R package and a website that implements statistical tests for significant transcription factor motif cooperativity between enhancer-promoter interactions. We conducted controlled experiments under realistic simulated data from ChIP-seq to confirm spatzie is capable of discovering co-enriched motif interactions even in noisy conditions. We then use spatzie to investigate cell type specific transcription factor cooperativity within recent human ChIA-PET enhancer-promoter interaction data. The method is available online at https://spatzie.mit.edu.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Supervised learning of enhancer-promoter specificity based on genome-wide perturbation studies highlights areas for improvement in learning.Bioinformatics. 2024 Jun 3;40(6):btae367. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae367. Bioinformatics. 2024. PMID: 38870532 Free PMC article.
-
High resolution mapping of enhancer-promoter interactions.PLoS One. 2015 May 13;10(5):e0122420. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122420. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25970635 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancer identification in mouse embryonic stem cells using integrative modeling of chromatin and genomic features.BMC Genomics. 2012 Apr 26;13:152. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-152. BMC Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22537144 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factors: from enhancer binding to developmental control.Nat Rev Genet. 2012 Sep;13(9):613-26. doi: 10.1038/nrg3207. Epub 2012 Aug 7. Nat Rev Genet. 2012. PMID: 22868264 Review.
-
Utility of next-generation RNA-sequencing in identifying chimeric transcription involving human endogenous retroviruses.APMIS. 2016 Jan-Feb;124(1-2):127-39. doi: 10.1111/apm.12477. APMIS. 2016. PMID: 26818267 Review.
Cited by
-
Guidelines on the performance evaluation of motif recognition methods in bioinformatics.Front Genet. 2023 Feb 7;14:1135320. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1135320. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36824436 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
DLoopCaller: A deep learning approach for predicting genome-wide chromatin loops by integrating accessible chromatin landscapes.PLoS Comput Biol. 2022 Oct 7;18(10):e1010572. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010572. eCollection 2022 Oct. PLoS Comput Biol. 2022. PMID: 36206320 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kosak S.T., Groudine M.. Form follows function: the genomic organization of cellular differentiation. Genes Dev. 2004; 18:1371–1384. - PubMed
-
- Lanctôt C., Cheutin T., Cremer M., Cavalli G., Cremer T.. Dynamic genome architecture in the nuclear space: regulation of gene expression in three dimensions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007; 8:104–115. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

