TRPM7 silencing modulates glucose metabolic reprogramming to inhibit the growth of ovarian cancer by enhancing AMPK activation to promote HIF-1α degradation
- PMID: 35101076
- PMCID: PMC8802454
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-022-02252-1
TRPM7 silencing modulates glucose metabolic reprogramming to inhibit the growth of ovarian cancer by enhancing AMPK activation to promote HIF-1α degradation
Abstract
Background: Tumor cell metabolic reprogramming is crucial for the malignant behavior of cancer cells by promoting their proliferation. However, little is known on how transient receptor potential 7 (TRPM7) modulates metabolic reprogramming in ovarian cancer.
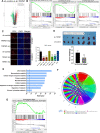
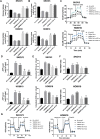
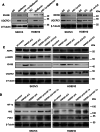
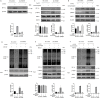
Methods: The effects of TRPM7 silencing on transcriptome profile, glucose uptake, lactic acid production, extracellular acidification rate (ECAR), oxygen consumption rate (OCR), intracellular ROS and ATP levels, and NAD+/NADH ratios in ovarian cancer cells were examined. The impacts of TRPM7 silencing on the levels of glycolysis-related HK2, PDK1 and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS)-related IDH3B and UQCRC1, HIF-1α expression and AMPK phosphorylation were determined in ovarian cancer. The effect of AMPK activity on HIF-1α ubiquitination degradation was investigated in ovarian cancer cells.
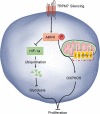
Results: Compared with the control, TRPM7 silencing suppressed the proliferation of ovarian cancer cells by shifting preferable glycolysis to OXPHOS. In parallel, TRPM7 silencing decreased the glucose uptake of tumor-bearing mice and TRPM7 levels were negatively correlated with IDH3B and UQCRC1, but positively with HK2 and PDK1 expression in ovarian cancer tissues. Mechanistically, TRPM7 silencing significantly increased AMPK phosphorylation and decreased HIF-1α protein levels in ovarian cancer, particularly in HIF-1α silencing cells. The shifting from glycolysis to OXPHOS by TRPM7 silencing was abrogated by HIF-1α over-expression and impaired by inhibiting AMPK activity in ovarian cancer cells. Moreover, enhanced AMPK activation inhibited glycolysis, which was abrogated by HIF-1α over-expression in ovarian cancer cells. Moreover, the enhanced AMPK activation promoted HIF-1α ubiquitination degradation.
Conclusions: TRPM7 silencing enhanced AMPK activation to shift glycolysis to oxidative phosphorylation by promoting HIF-1α ubiquitination degradation in ovarian cancer. Hence, TRPM7 may be a therapeutic target for intervention of ovarian cancer.
Keywords: AMPK; Glycolysis; HIF-1α; Ovarian cancer; Oxidative phosphorylation; TRPM7; Ubiquitination.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no potential competing interest.
Figures



References
-
- Amin RW, et al. Patterns of ovarian cancer and uterine cancer mortality and incidence in the contiguous USA. Sci Total Environ. 2019;697:134128. - PubMed
-
- Kinnaird A, et al. Metabolic control of epigenetics in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016;16(11):694–707. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144(5):646–674. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

