The regional sequestration of heterochromatin structural proteins is critical to form and maintain silent chromatin
- PMID: 35101096
- PMCID: PMC8805269
- DOI: 10.1186/s13072-022-00435-w
The regional sequestration of heterochromatin structural proteins is critical to form and maintain silent chromatin
Abstract
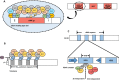
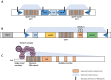
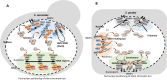
Budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe are good models for heterochromatin study. In S. pombe, H3K9 methylation and Swi6, an ortholog of mammalian HP1, lead to heterochromatin formation. However, S. cerevisiae does not have known epigenetic silencing markers and instead has Sir proteins to regulate silent chromatin formation. Although S. cerevisiae and S. pombe form and maintain heterochromatin via mechanisms that appear to be fundamentally different, they share important common features in the heterochromatin structural proteins. Heterochromatin loci are localized at the nuclear periphery by binding to perinuclear membrane proteins, thereby producing distinct heterochromatin foci, which sequester heterochromatin structural proteins. In this review, we discuss the nuclear peripheral anchoring of heterochromatin foci and its functional relevance to heterochromatin formation and maintenance.
Keywords: Heterochromatin structural proteins; SIR complex; Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Schizosaccharomyces pombe; Swi6.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Grewal SI, Jia S. Heterochromatin revisited. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:35–46. - PubMed
-
- Huisinga KL, et al. The contradictory definitions of heterochromatin: transcription and silencing. Chromosoma. 2006;115:110–122. - PubMed
-
- Richards EJ, Elgin SC. Epigenetic codes for heterochromatin formation and silencing: rounding up the usual suspects. Cell. 2002;108:489–500. - PubMed
-
- Bannister AJ, et al. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature. 2001;410:120–124. - PubMed
-
- Lachner M, et al. Methylation of histone H3 lysine 9 creates a binding site for HP1 proteins. Nature. 2001;410:116–120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

