Identification of selenoprotein O substrates using a biotinylated ATP analog
- PMID: 35101215
- PMCID: PMC9817423
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.mie.2021.10.001
Identification of selenoprotein O substrates using a biotinylated ATP analog
Abstract
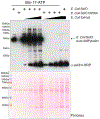
Selenoprotein O is one of 25 human selenoproteins that incorporate the 21st amino acid selenocysteine. Recent studies have revealed a previously undocumented mechanism of redox regulation by which SelO protects cells from oxidative damage. SelO catalyzes the covalent addition of AMP from ATP to the hydroxyl side chain of protein substrates in a post translational modification known as AMPylation. Although AMPylation was discovered over 50 years ago, methods to detect and enrich substrates are limited. Here, we describe protocols to clone, purify, and identify the substrates of bacterial SelO using a biotinylated ATP analog. Identification of SelO substrates and the functional consequences of AMPylation will illuminate the significance of this evolutionarily conserved selenoprotein.
Keywords: AMPylation; Adenylylation; Mitochondria; Oxidative stress; Pseudokinase; SelenoO; ydiU.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Protein AMPylation by an Evolutionarily Conserved Pseudokinase.Cell. 2018 Oct 18;175(3):809-821.e19. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.08.046. Epub 2018 Sep 27. Cell. 2018. PMID: 30270044 Free PMC article.
-
A novel protein kinase-like domain in a selenoprotein, widespread in the tree of life.PLoS One. 2012;7(2):e32138. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032138. Epub 2012 Feb 16. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22359664 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of mammalian selenoprotein o: a redox-active mitochondrial protein.PLoS One. 2014 Apr 21;9(4):e95518. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095518. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24751718 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of protein function by reversible methionine oxidation and the role of selenoprotein MsrB1.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015 Oct 1;23(10):814-22. doi: 10.1089/ars.2015.6385. Epub 2015 Jul 16. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2015. PMID: 26181576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Common modifications of selenocysteine in selenoproteins.Essays Biochem. 2020 Feb 17;64(1):45-53. doi: 10.1042/EBC20190051. Essays Biochem. 2020. PMID: 31867620 Review.
Cited by
-
Selenium metabolism and selenoproteins function in brain and encephalopathy.Sci China Life Sci. 2025 Mar;68(3):628-656. doi: 10.1007/s11427-023-2621-7. Epub 2024 Nov 12. Sci China Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 39546178 Review.
-
A repurposed AMP binding domain reveals mitochondrial protein AMPylation as a regulator of cellular metabolism.Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 23;16(1):7863. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-63014-z. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40849408 Free PMC article.
-
Selenoproteins and the senescence-associated epitranscriptome.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022 Dec;247(23):2090-2102. doi: 10.1177/15353702221116592. Epub 2022 Aug 29. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2022. PMID: 36036467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
deep-Sep: a deep learning-based method for fast and accurate prediction of selenoprotein genes in bacteria.mSystems. 2025 Apr 22;10(4):e0125824. doi: 10.1128/msystems.01258-24. Epub 2025 Mar 10. mSystems. 2025. PMID: 40062874 Free PMC article.
-
Selenoprotein O Promotes Melanoma Metastasis and Regulates Mitochondrial Complex II Activity.Cancer Res. 2025 Mar 3;85(5):942-955. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-2194. Cancer Res. 2025. PMID: 39700395 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

