Laser induced breakdown spectroscopy for the rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 immune response in plasma
- PMID: 35102204
- PMCID: PMC8803875
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-05509-z
Laser induced breakdown spectroscopy for the rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 immune response in plasma
Abstract
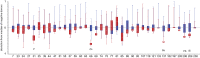
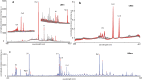
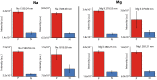
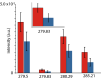
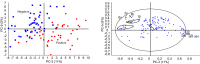
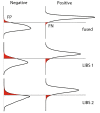
As the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic persists, methods that can quickly and reliably confirm infection and immune status is extremely urgently and critically needed. In this contribution we show that combining laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) with machine learning can distinguish plasma of donors who previously tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 by RT-PCR from those who did not, with up to 95% accuracy. The samples were also analyzed by LIBS-ICP-MS in tandem mode, implicating a depletion of Zn and Ba in samples of SARS-CoV-2 positive subjects that inversely correlate with CN lines in the LIBS spectra.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Nationwide Commercial Laboratory Seroprevalence Survey, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#national-lab (Accessed May 2021).
-
- SeroTracker by the SeroTracker Collaboration. https://serotracker.com/en/Analyze (Accessed May 2021).
-
- Cremers DA, Radziemski LJ. Handbook of Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. Wiley; 2013. p. 407.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

