N6-substituated adenosine analog J4 attenuates anxiety-like behaviors in mice
- PMID: 35102423
- PMCID: PMC9063204
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-022-06079-8
N6-substituated adenosine analog J4 attenuates anxiety-like behaviors in mice
Abstract
Rationale: Withdrawal from chronic alcohol exposure produces various physical and mental withdrawal symptoms. Activation of adenosine receptors is known to inhibit withdrawal-induced excitation. However, limited studies investigate how adenosine analogs may prove helpful tools to alleviate alcohol withdrawal-related affective behaviors.
Objectives: This study aimed to investigate the effects of J4 compared with saline using the mice vapor or voluntary ethanol drinking model on behavioral endpoints representing ethanol-withdrawal negative emotionality commonly observed during abstinence from chronic alcohol use.
Methods: We subjected C57BL/6 J mice to chronic intermittent ethanol (CIE) exposure schedule to investigate how 72-h withdrawal from alcohol alters affective-like behavior. Next, we determined how treatment with J4, a second-generation adenosine analog, influenced affective behaviors produced by alcohol withdrawal. Finally, we determined how J4 treatment alters voluntary ethanol drinking using the two-bottle-choice drinking paradigm.
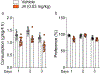
Results: Our results show that 72-h withdrawal from chronic intermittent ethanol exposure produces limited affective-like disturbances in male C57BL/6 J mice exposed to 4 cycles ethanol vapor. Most importantly, J4 treatment irrespective of ethanol exposure decreases innate anxiety-like behavior in mice.
Conclusions: Withdrawal from chronic intermittent ethanol exposure and subsequent behavioral testing 72 h later produces minimal affective-like behavior. J4 treatment did however reduce marble-burying behavior and increased time spent in open arms of the elevated plus maze, suggesting J4 may be useful as a general anxiolytic.
Keywords: Adenosine; Elevated-plus maze; J4; Marble-burying; Two-bottle choice.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
D-S Choi is a scientific advisory board member to Peptron Inc. Peptron had no role in preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript. Y Chern holds patents on treating neurodegenerative diseases and pain by J4. All the other authors declare no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

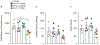

References
-
- Association AP (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders : DSM-5. American Psychiatric Association, Arlington, VA
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

