Mini-implant assisted rapid palatal expansion (MARPE) effects on adult obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and quality of life: a multi-center prospective controlled trial
- PMID: 35102477
- PMCID: PMC8804045
- DOI: 10.1186/s40510-021-00397-x
Mini-implant assisted rapid palatal expansion (MARPE) effects on adult obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and quality of life: a multi-center prospective controlled trial
Abstract
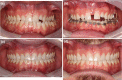
Introduction: Transverse maxillary deficiency is a high prevalent growth disorder within the adult population that may lead to serious health issues, such as detrimental malocclusions and higher risk of developing obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Mini-implant assisted rapid palatal expansion (MARPE), as it expands the mid-face and augment the nasal and oral cavities dimensions, may reduce the airflow resistance and thus play an important role on OSA therapy in some patients. The main objective of the present trial is to assess MARPE effects on the sleep and quality of life of non-obese adult OSA patients with transverse maxillary deficiency.
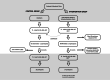
Methods: A total of 32 participants were divided into intervention and control groups. They underwent physical evaluation, Epworth Sleepiness Scale (EES) and Quebec Sleep Questionnaire (QSQ), cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) and home sleep testing (HST) for OSA before MARPE (T1) and 6 months after the intervention (T2).
Results: Questionnaires EES (daytime sleepiness) and QSQ (OSA-related quality of life) presented significant statistical differences between the groups. We also found clinical and statistical (p < 0.01) differences between the groups regarding the apnea/hypopnea index (AHI), as well as others HST parameters (mean oxygen saturation and snoring duration).
Conclusion: In our sample, MARPE (without any auxiliary osteotomy) showed a good success rate (85%) and promoted important occlusal and respiratory benefits. We observed important daytime sleepiness and OSA-related quality of life improvement, as well as the AHI (65.3%), oxygen saturation and snoring duration.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
One of the authors (Won Moon) declares he has one patent concerning the expander used on the study, the Maxillary Skeletal Expander (MSE).
Figures


References
-
- Pankow W, Lies A, Lohmann FW. Sleep-disordered breathing and hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2000;343:966. - PubMed
-
- Hu FB, Willett WC, Manson JE, Colditz GA, Rimm EB, Speizer FE, et al. Snoring and risk of cardiovascular disease in women. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000;35:308–313. - PubMed
-
- Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, Skatrud J, Weber S, Badr S. The occurrence of sleep-disordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N Engl J Med. 1993;328:1230–1235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

