A Combination of Caffeine, TeaCrine® (Theacrine), and Dynamine® (Methylliberine) Increases Cognitive Performance and Reaction Time Without Interfering With Mood in Adult Male Egamers
- PMID: 35103121
- PMCID: PMC8768451
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.20534
A Combination of Caffeine, TeaCrine® (Theacrine), and Dynamine® (Methylliberine) Increases Cognitive Performance and Reaction Time Without Interfering With Mood in Adult Male Egamers
Abstract
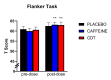
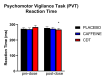
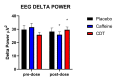
Background Involvement in video game activities and competitive video gaming (esports) is a rapidly growing field. Moreover, there is a marked interest in identifying nutritional supplements to safely improve egamer performance. Methodology We conducted a repeated-measure, randomized crossover study to compare the effects of caffeine (125 mg), caffeine (125 mg) + Dynamine® (75 mg) + TeaCrine® (50 mg) (CDT), and matched placebo across three testing sessions (one week apart) among 50 young male egamers. We tested the effect of each product on multiple measures of cognition, self-reported mood (anxiety, alertness, and headache), and biomarkers of arousal (cortisol and salivary alpha-amylase). We also measured electroencephalogram power during the cognitive tasks. Finally, we tested whether individual differences in xenobiotic metabolism would affect the study outcome measures by genotyping each participant for cytochrome P450 1A2*1F (CYP1A2*1F) allele status. Results Compared to pre-dose, CDT improved performance on the Flanker Test of Inhibitory Control and improved reaction time on the Psychomotor Vigilance Task post-dose. Compared to the placebo, caffeine increased self-reported anxiety whereas the CDT combination increased self-reported alertness. Compared to the CDT combination, caffeine increased self-reported headaches. Physiological measures suggested that increases in delta EEG power and cortisol production are associated with the effects observed in the CDT condition to optimize certain aspects of egamer performance. CYP1A2*1F allele status did not moderate outcome variables between conditions in this study. Conclusions CDT is a safe and effective product for improving cognitive performance among egamers without increasing self-reported anxiety or headaches. EEG changes demonstrate that CDT increased attention to internal processing (i.e., increased cortical delta power) and potentially increased cognitive control (i.e., increased cortical theta frequency), while the increases in cortisol suggest increased energy mobilization. Future work should aim to clarify the physiological underpinnings of CDT-induced changes in performance and examine the effects of CDT under naturalistic egamer conditions.
Keywords: attention; caffeine; cognition; dynamine; egamer; teacrine.
Copyright © 2021, Tartar et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Jose Antonio, PhD, is the CEO of the International Society of Sports Nutrition (ISSN). The ISSN is an academic non-profit (501c3) that has previously received sponsorship money from Compound Solutions.
Figures
References
-
- Gamer's health guide: optimizing performance, recognizing hazards, and promoting wellness in esports. Emara AK, Ng MK, Cruickshank JA, Kampert MW, Piuzzi NS, Schaffer JL, King D. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2020;19:537–545. - PubMed
-
- The effects of action video game experience on the time course of inhibition of return and the efficiency of visual search. Castel AD, Pratt J, Drummond E. Acta Psychol (Amst) 2005;119:217–230. - PubMed
-
- Action video game modifies visual selective attention. Green CS, Bavelier D. Nature. 2003;423:534–537. - PubMed
-
- Action video gaming and cognitive control: playing first person shooter games is associated with improvement in working memory but not action inhibition. Colzato LS, van den Wildenberg WP, Zmigrod S, Hommel B. Psychol Res. 2013;77:234–239. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
