Bacteriological Profile of Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Detection of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase Producers in a Tertiary Care Hospital
- PMID: 35103172
- PMCID: PMC8778651
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.20596
Bacteriological Profile of Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Detection of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase Producers in a Tertiary Care Hospital
Abstract
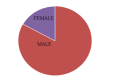
Introduction Diabetic foot infection is the most dreaded complication of diabetes mellitus and the commonest cause of hospitalization and limb amputation. Identification of the causative agent responsible for diabetic foot infection and the earliest initiation of appropriate antimicrobial therapy are vital for the control and prevention of the complication of diabetic foot ulcers. Therefore, we conducted this study to determine the bacteriological profile of diabetic foot ulcers and to detect methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) producers in our institute. Methodology During the study period, samples were collected from the foot ulcers of 100 patients at the Diabetic Outpatient Department. The samples were processed according to the standard laboratory protocol, and bacterial isolates were identified. Antibiotic susceptibility testing was performed using the modified Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion technique, and results were interpreted according to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute guidelines (CLSI 2016). A phenotypic test for MRSA detection was performed using cefoxitin (30 μg) disk. Results The highest incidence of diabetic foot ulcers was observed in patients aged 41-50 years. There were 83 men and 17 women, with a male to female ratio of 4.882. Of the 100 collected samples, 73 were positive for microbial growth, and 27 samples showed no growth. Of the 73 positive cultures, monomicrobial infection was found in 48 patients, and polymicrobial infection was found in 25 patients. Gram-positive pathogens were isolated from 34 patients, and gram-negative microbes were isolated from 64 patients. Among all collected isolates (n=100), Staphylococcus aureus was the most predominant organism and Acinetobacter species was the least common (only two isolates). Among the gram-negative bacteria, Pseudomonas aeruginosa was predominant. All the isolated gram-positive bacteria were susceptible to vancomycin. Gram-negative bacteria were highly susceptible to colistin with the exception of Proteus species which is intrinsically resistant to colistin and it is not reported for Proteus species. ESBL producers were primarily found among Klebsiella species isolates (22.22%). Among 29 S. aureus isolates, 8 (27.5%) were found to be MRSA producers. Conclusion Based on the bacteriological profile of diabetic foot ulcers, S. aureus among the gram-positive isolates and P. aeruginosa among the gram-negative isolates were the predominant pathogens. Infections caused by multidrug-resistant bacteria such as MRSA and ESBL producers have been reported with increasing frequency. According to the antibiotic susceptibility pattern, treatment can be initiated, continued, or altered, thereby reducing morbidity in patients with diabetic foot ulcers.
Keywords: antimicrobial therapy; diabetic foot infection; esbl; mrsa; phenotypic test.
Copyright © 2021, Selvarajan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Similar articles
-
Prevalence of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus, multidrug resistant and extended spectrum β-lactamase producing gram negative bacilli causing wound infections at a tertiary care hospital of Nepal.Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2018 Oct 8;7:121. doi: 10.1186/s13756-018-0408-z. eCollection 2018. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. 2018. PMID: 30338059 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and antibiotic susceptibility of microorganisms isolated from diabetic foot ulcers: A pathological aspect.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Dec 7;25(1):53. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11752. eCollection 2023 Jan. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 36588808 Free PMC article.
-
Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Infection of Diabetic Foot Ulcers at a Tertiary Care Hospital in Accra, Ghana.Pathogens. 2021 Jul 24;10(8):937. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10080937. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34451401 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial Infection and Antibiotic Susceptibility of Diabetic Foot Ulcer in China: Literature Review.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 May 19;13:881659. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.881659. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35663325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systematic Review of the Microbial Landscape of Diabetic Foot Ulcers in Uganda.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Jan 13;17:143-151. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S446838. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 38234374 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Relative Abundance and Detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from Chronic Wound Infections Globally.Microorganisms. 2023 May 5;11(5):1210. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11051210. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37317184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Microbial Diversity and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Profile Underlying Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis: A Retrospective Study Conducted in North Queensland, Australia.Foot Ankle Orthop. 2024 Sep 30;9(3):24730114241281503. doi: 10.1177/24730114241281503. eCollection 2024 Jul. Foot Ankle Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39380709 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated From Diabetic Foot Ulcers in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Mysuru, South India.Cureus. 2024 Oct 1;16(10):e70605. doi: 10.7759/cureus.70605. eCollection 2024 Oct. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39483566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1047–1053. - PubMed
-
- Obesity and diabetes in the developing world--a growing challenge. Hossain P, Kawar B, El Nahas M. N Engl J Med. 2007;356:213–215. - PubMed
-
- Diabetic foot disease—incidence and risk factors: a clinical study. Sharma R, Kapila R, Sharma AK, Mann J. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2016;3:41–46.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources