A single mRNA vaccine dose in COVID-19 patients boosts neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and variants of concern
- PMID: 35103254
- PMCID: PMC8668345
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100486
A single mRNA vaccine dose in COVID-19 patients boosts neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 and variants of concern
Abstract
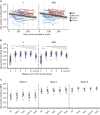
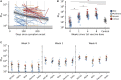
The urgent need for, but limited availability of, SARS-CoV-2 vaccines worldwide has led to widespread consideration of dose-sparing strategies. Here, we evaluate the SARS-CoV-2-specific antibody responses following BNT162b2 vaccination in 150 previously SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals from a population-based cohort. One week after first vaccine dose, spike protein antibody levels are 27-fold higher and neutralizing antibody titers 12-fold higher, exceeding titers of fully vaccinated SARS-CoV-2-naive controls, with minimal additional boosting after the second dose. Neutralizing antibody titers against four variants of concern increase after vaccination; however, overall neutralization breadth does not improve. Pre-vaccination neutralizing antibody titers and time since infection have the largest positive effect on titers following vaccination. COVID-19 severity and the presence of comorbidities have no discernible impact on vaccine response. In conclusion, a single dose of BNT162b2 vaccine up to 15 months after SARS-CoV-2 infection offers higher neutralizing antibody titers than 2 vaccine doses in SARS-CoV-2-naive individuals.
Keywords: BNT162b2; COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; antibody response; mRNA vaccine; neutralization; previous infection; response predictors; variants.
© 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Omer S.B., Yildirim I., Forman H.P. Herd Immunity and Implications for SARS-CoV-2 Control. JAMA. 2020;324:2095–2096. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

