Infection or a third dose of mRNA vaccine elicits neutralizing antibody responses against SARS-CoV-2 in kidney transplant recipients
- PMID: 35103481
- PMCID: PMC8939774
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abl6141
Infection or a third dose of mRNA vaccine elicits neutralizing antibody responses against SARS-CoV-2 in kidney transplant recipients
Abstract
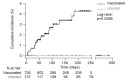
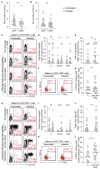
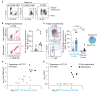
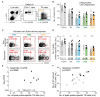
Transplant recipients, who receive therapeutic immunosuppression to prevent graft rejection, are characterized by high coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-related mortality and defective response to vaccines. We observed that previous infection with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), but not the standard two-dose regimen of vaccination, provided protection against symptomatic COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients. We therefore compared the cellular and humoral immune responses of these two groups of patients. Neutralizing anti-receptor-binding domain (RBD) immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies were identified as the primary correlate of protection for transplant recipients. Analysis of virus-specific B and T cell responses suggested that the generation of neutralizing anti-RBD IgG may have depended on cognate T-B cell interactions that took place in germinal center, potentially acting as a limiting checkpoint. High-dose mycophenolate mofetil, an immunosuppressive drug, was associated with fewer antigen-specific B and T follicular helper (TFH) cells after vaccination; this was not observed in patients recently infected with SARS-CoV-2. Last, we observed that, in two independent prospective cohorts, administration of a third dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine restored neutralizing titers of anti-RBD IgG in about 40% of individuals who had not previously responded to two doses of vaccine. Together, these findings suggest that a third dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine improves the RBD-specific responses of transplant patients treated with immunosuppressive drugs.
Figures


References
-
- Zhu N., Zhang D., Wang W., Li X., Yang B., Song J., Zhao X., Huang B., Shi W., Lu R., Niu P., Zhan F., Ma X., Wang D., Xu W., Wu G., Gao G. F., Tan W.; China Novel Coronavirus Investigating and Research Team , A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019. N. Engl. J. Med. 382, 727–733 (2020). 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- COVID-19 situation update worldwide, as of week 1, updated 13 January 2022. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control, (available at https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/geographical-distribution-2019-ncov-cases).
-
- Williamson E. J., Walker A. J., Bhaskaran K., Bacon S., Bates C., Morton C. E., Curtis H. J., Mehrkar A., Evans D., Inglesby P., Cockburn J., McDonald H. I., MacKenna B., Tomlinson L., Douglas I. J., Rentsch C. T., Mathur R., Wong A. Y. S., Grieve R., Harrison D., Forbes H., Schultze A., Croker R., Parry J., Hester F., Harper S., Perera R., Evans S. J. W., Smeeth L., Goldacre B., Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY. Nature 584, 430–436 (2020). 10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Caillard S., Anglicheau D., Matignon M., Durrbach A., Greze C., Frimat L., Thaunat O., Legris T., Moal V., Westeel P. F., Kamar N., Gatault P., Snanoudj R., Sicard A., Bertrand D., Colosio C., Couzi L., Chemouny J. M., Masset C., Blancho G., Bamoulid J., Duveau A., Bouvier N., Chavarot N., Grimbert P., Moulin B., Le Meur Y., Hazzan M.; French SOT COVID Registry , An initial report from the French SOT COVID Registry suggests high mortality due to COVID-19 in recipients of kidney transplants. Kidney Int. 98, 1549–1558 (2020). 10.1016/j.kint.2020.08.005 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jager K. J., Kramer A., Chesnaye N. C., Couchoud C., Sánchez-Álvarez J. E., Garneata L., Collart F., Hemmelder M. H., Ambühl P., Kerschbaum J., Legeai C., Del Pino Y Pino M. D., Mircescu G., Mazzoleni L., Hoekstra T., Winzeler R., Mayer G., Stel V. S., Wanner C., Zoccali C., Massy Z. A., Results from the ERA-EDTA Registry indicate a high mortality due to COVID-19 in dialysis patients and kidney transplant recipients across Europe. Kidney Int. 98, 1540–1548 (2020). 10.1016/j.kint.2020.09.006 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

