Sugar conundrum in plant-pathogen interactions: roles of invertase and sugar transporters depend on pathosystems
- PMID: 35104311
- PMCID: PMC8982439
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/erab562
Sugar conundrum in plant-pathogen interactions: roles of invertase and sugar transporters depend on pathosystems
Abstract
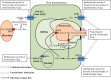
It has been increasingly recognized that CWIN (cell wall invertase) and sugar transporters including STP (sugar transport protein) and SWEET (sugar will eventually be exported transporters) play important roles in plant-pathogen interactions. However, the information available in the literature comes from diverse systems and often yields contradictory findings and conclusions. To solve this puzzle, we provide here a comprehensive assessment of the topic. Our analyses revealed that the regulation of plant-microbe interactions by CWIN, SWEET, and STP is conditioned by the specific pathosystems involved. The roles of CWINs in plant resistance are largely determined by the lifestyle of pathogens (biotrophs versus necrotrophs or hemibiotrophs), possibly through CWIN-mediated salicylic acid or jasmonic acid signaling and programmed cell death pathways. The up-regulation of SWEETs and STPs may enhance or reduce plant resistance, depending on the cellular sites from which pathogens acquire sugars from the host cells. Finally, plants employ unique mechanisms to defend against viral infection, in part through a sugar-based regulation of plasmodesmatal development or aperture. Our appraisal further calls for attention to be paid to the involvement of microbial sugar metabolism and transport in plant-pathogen interactions, which is an integrated but overlooked component of such interactions.
Keywords: Bacteria; STP; SWEET; fungi; invertase; pathogen; sugar metabolism; sugar signaling; sugar transport; virus.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Experimental Biology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CWIN-sugar transporter nexus is a key component for reproductive success.J Plant Physiol. 2022 Jan;268:153572. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2021.153572. Epub 2021 Nov 18. J Plant Physiol. 2022. PMID: 34839101
-
Integrating Sugar Metabolism With Transport: Elevation of Endogenous Cell Wall Invertase Activity Up-Regulates SlHT2 and SlSWEET12c Expression for Early Fruit Development in Tomato.Front Genet. 2020 Oct 19;11:592596. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.592596. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 33193736 Free PMC article.
-
From Functional Characterization to the Application of SWEET Sugar Transporters in Plant Resistance Breeding.J Agric Food Chem. 2022 May 4;70(17):5273-5283. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c00582. Epub 2022 Apr 21. J Agric Food Chem. 2022. PMID: 35446562 Review.
-
Plant SWEETs: from sugar transport to plant-pathogen interaction and more unexpected physiological roles.Plant Physiol. 2021 Jun 11;186(2):836-852. doi: 10.1093/plphys/kiab127. Plant Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33724398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant SWEET Family of Sugar Transporters: Structure, Evolution and Biological Functions.Biomolecules. 2022 Jan 25;12(2):205. doi: 10.3390/biom12020205. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35204707 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The transcriptional response to yellow and wilt disease, caused by race 6 of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Ciceris in two contrasting chickpea cultivars.BMC Genomics. 2025 Feb 4;26(1):106. doi: 10.1186/s12864-025-11308-3. BMC Genomics. 2025. PMID: 39905311 Free PMC article.
-
Multifactor transcriptional profiling of potato during 2,4-D-induced resistance to common scab disease.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Aug 18;16:1641317. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1641317. eCollection 2025. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 40901548 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-Seq Analysis and Candidate Gene Mining of Gossypium hirsutum Stressed by Verticillium dahliae Cultured at Different Temperatures.Plants (Basel). 2024 Sep 25;13(19):2688. doi: 10.3390/plants13192688. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409558 Free PMC article.
-
The link between changing in host carbon allocation and resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae: a possible tactic for mitigating the rice blast fungus.Plant Signal Behav. 2024 Dec 31;19(1):2326870. doi: 10.1080/15592324.2024.2326870. Epub 2024 Mar 11. Plant Signal Behav. 2024. PMID: 38465846 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive transcriptome analyses of Fusarium-infected root xylem tissues to decipher genes involved in chickpea wilt resistance.3 Biotech. 2023 Dec;13(12):390. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03803-9. Epub 2023 Nov 7. 3 Biotech. 2023. PMID: 37942053 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berger S, Sinha AK, Roitsch T.. 2007. Plant physiology meets phytopathology: plant primary metabolism and plant pathogen interactions. Journal of Experimental Botany 58, 4019–4026. - PubMed
-
- Bezrutczyk M, Yang J, Eom JS, et al. . 2018. Sugar flux and signaling in plant–microbe interactions. The Plant Journal 93, 675–685. - PubMed
-
- Bisson LF, Coons DM, Kruckeberg AL, Lewis DA.. 1993. Yeast sugar transporters. Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 28, 259–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

