IgG anti-spike antibody levels in healthcare workers with and without prior COVID-19 up to 3 months after BNT162b2 vaccination
- PMID: 35104720
- PMCID: PMC8761117
- DOI: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2022.115638
IgG anti-spike antibody levels in healthcare workers with and without prior COVID-19 up to 3 months after BNT162b2 vaccination
Abstract
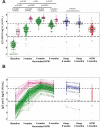
We report IgG anti-spike levels up to 3 months after vaccination with 2 doses of BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in healthcare workers (HCW). The antibody response was significantly stronger in previously infected vaccinated HCW compared to uninfected HCW, and stronger after vaccination compared to (mostly) mild natural infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; COVID-19 testing; IgG; Immunoassay; SARS-CoV-2; Spike; Vaccination.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

