How patients with multiple sclerosis acquire disability
- PMID: 35104840
- PMCID: PMC9536294
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awac016
How patients with multiple sclerosis acquire disability
Abstract
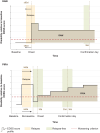
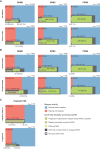
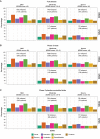
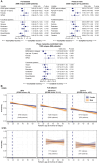
Patients with multiple sclerosis acquire disability either through relapse-associated worsening (RAW) or progression independent of relapse activity (PIRA). This study addresses the relative contribution of relapses to disability worsening over the course of the disease, how early progression begins and the extent to which multiple sclerosis therapies delay disability accumulation. Using the Novartis-Oxford multiple sclerosis (NO.MS) data pool spanning all multiple sclerosis phenotypes and paediatric multiple sclerosis, we evaluated ∼200 000 Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) transitions from >27 000 patients with ≤15 years follow-up. We analysed three datasets: (i) A full analysis dataset containing all observational and randomized controlled clinical trials in which disability and relapses were assessed (n = 27 328); (ii) all phase 3 clinical trials (n = 8346); and (iii) all placebo-controlled phase 3 clinical trials (n = 4970). We determined the relative importance of RAW and PIRA, investigated the role of relapses on all-cause disability worsening using Andersen-Gill models and observed the impact of the mechanism of worsening and disease-modifying therapies on the time to reach milestone disability levels using time continuous Markov models. PIRA started early in the disease process, occurred in all phenotypes and became the principal driver of disability accumulation in the progressive phase of the disease. Relapses significantly increased the hazard of all-cause disability worsening events; following a year in which relapses occurred (versus a year without relapses), the hazard increased by 31-48% (all P < 0.001). Pre-existing disability and older age were the principal risk factors for incomplete relapse recovery. For placebo-treated patients with minimal disability (EDSS 1), it took 8.95 years until increased limitation in walking ability (EDSS 4) and 18.48 years to require walking assistance (EDSS 6). Treating patients with disease-modifying therapies delayed these times significantly by 3.51 years (95% confidence limit: 3.19, 3.96) and 3.09 years (2.60, 3.72), respectively. In patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis, those who worsened exclusively due to RAW events took a similar length of time to reach milestone EDSS values compared with those with PIRA events; the fastest transitions were observed in patients with PIRA and superimposed relapses. Our data confirm that relapses contribute to the accumulation of disability, primarily early in multiple sclerosis. PIRA begins in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis and becomes the dominant driver of disability accumulation as the disease evolves. Pre-existing disability and older age are the principal risk factors for further disability accumulation. The use of disease-modifying therapies delays disability accrual by years, with the potential to gain time being highest in the earliest stages of multiple sclerosis.
Keywords: disability; disease progression; multiple sclerosis; progression independent of relapse activity; relapse.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Conflict of interest statement
F.L. reports as sources of funding for research: Novartis, Actelion, Biogen, Sanofi, NMSS, NIH and Brainstorm Cell Therapeutics; consulting agreements/advisory boards/DSMB: Biogen, EMD Serono, Novartis, Teva, Actelion/Janssen, Sanofi/Genzyme, Acorda, Roche/Genentech, MedImmune/Viela Bio, Receptos/Celgene/BMS, TG Therapeutics, Medday, Atara Biotherapeutics, Mapi Pharma, Apitope, Orion Biotechnology, Brainstorm Cell Therapeutics, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, GW Pharma, Mylan, Immunic, Population Council, Avotres, Neurogene, Banner Life Sciences, Labcorp, Entelexo Biotherapeutics and NeuraLight; stock options: Avotres and NeuraLight; Speaker: Sanofi (non-promotional). D.A. reports consulting fees from Albert Charitable Trust, Alexion Pharma, Biogen, Celgene, Frequency Therapeutics, Genentech, Med-Ex Learning, Merck, Novartis, Population Council, Receptos, Roche and Sanofi-Aventis; grants from Biogen, Immunotec and Novartis and an equity interest in NeuroRx. H.W. receives honoraria for acting as a member of Scientific Advisory Boards for Biogen, Genzyme, Merck Serono, Novartis, Roche Pharma AG and Sanofi-Aventis and UCB; as well as speaker honoraria and travel support from Alexion, Biogen, Biologix, Cognomed, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Gemeinnützige Hertie-Stiftung, Merck, Novartis, Roche Pharma AG, Genzyme, Teva and WebMD Global. H.W. is acting as a paid consultant for Actelion, Argenx, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, EMD Serono, Idorsia, IGES, Immunic, Immunovant, Janssen, Johnson & Johnson, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi, the Swiss Multiple Sclerosis Society and UCB. His research is funded by the German Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF), Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), Else Kröner Fresenius Foundation, Fresenius Foundation, the European Union, Hertie Foundation, NRW Ministry of Education and Research, Interdisciplinary Center for Clinical Studies (IZKF) Muenster and Biogen, GlaxoSmithKline, Roche Pharma AG and Sanofi-Genzyme. T.C. reports consulting fees from Biogen Idec, Novartis and Genentech; grants from Novartis, Octave Bioscience and Tiziana Life Sciences; all outside the submitted work. R.B. has served as a consultant for AstraZeneca, Biogen, EMD Serono, Genzyme, Genentech, Novartis and VielaBio. He receives research support from Biogen, Genentech and Novartis. H.G., F.H. and T.N. report no competing interests. F.D. was a salaried employee of Novartis during manuscript development, but is no longer employed by Novartis and reports no competing interests. D.H., A.O., J.Č., P.A. and B.K. are employees of Novartis.
Figures
References
-
- Kappos L, Wolinsky JS, Giovannoni G, et al. Contribution of relapse-independent progression vs relapse-associated worsening to overall confirmed disability accumulation in typical relapsing multiple sclerosis in a pooled analysis of 2 randomized clinical trials. JAMA Neurol 2020;77(9):1132–1140. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vukusic S, Confavreux C. Prognostic factors for progression of disability in the secondary progressive phase of multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 2003;206(2):135–137. - PubMed
-
- Casserly C, Ebers GC. Relapses do not matter in relation to long-term disability. Mult Scler. 2011;17(12):1412–1414. - PubMed
-
- Confavreux C, Vukusic S, Moreau T, Adeleine P. Relapses and progression of disability in multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(20):1430–1438. - PubMed
-
- Scalfari A, Neuhaus A, Daumer M, Muraro PA, Ebers GC. Onset of secondary progressive phase and long-term evolution of multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2014;85(1):67–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

