Randomized double-blind clinical trial comparing safety and efficacy of the biosimilar BCD-021 with reference bevacizumab
- PMID: 35105329
- PMCID: PMC8808992
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-022-09243-7
Randomized double-blind clinical trial comparing safety and efficacy of the biosimilar BCD-021 with reference bevacizumab
Abstract
Background: BCD-021 is a bevacizumab biosimilar which was shown to be equivalent to reference bevacizumab in a wide panel of physicochemical studies as well as preclinical studies in vitro and in vivo. International multicenter phase III clinical trial was conducted to compare efficacy and safety of BCD-021 and reference bevacizumab in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in a first-line treatment of inoperable or advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
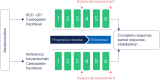
Methods: Patients with no previous treatment for advanced non-squamous NSCLC were randomly assigned 3:2 to BCD-021 or reference bevacizumab and were treated with bevacizumab + paclitaxel + carboplatin. Therapy continued for 6 cycles (every 3 weeks), until progression of the disease or unbearable toxicity. The primary study endpoint was the overall response rate. The study goal was to prove the equivalent efficacy of BCD-021 and reference bevacizumab. Equivalence margins for 95% CI for the difference in the overall response rates were set at [-18%; 18%], for 90% CI for the ratio of overall response rate were set at [67%; 150%].
Results: In total 357 patients were enrolled in the study, 212 in the BCD-021 group and 145 in the reference bevacizumab group. The ORR was 34.63% in the BCD-022 group and 33.82% in the reference bevacizumab group. Limits of 95% CI for the difference in overall response rates between the groups were [-9.47%; 11.09%]. Limits of 90% CI for the ratio of overall response rate between the groups were [79.6%; 131.73%]. For both approaches CI lied within predetermined equivalence margins. Profile of adverse events (AEs) was similar between the groups (any AEs were reported in 86.89% of patients in BCD-021 group and 89.05% of patients in reference group). No unexpected adverse reactions were reported throughout the study. No statistically significant differences regarding anti-drug antibody occurrence rate was found between BCD-022 (n=4; 1.96%) and comparator (n=5; 3.65%). Both drug products showed low occurrence rate and short life of anti-bevacizumab antibodies. Pharmacokinetics assessment after 1st and 6th study drug injection also demonstrated equivalent PK parameters by all outcome measures.
Conclusions: Thus, the results of this study demonstrated therapeutic equivalence of bevacizumab biosimilar BCD-021 and referent bevacizumab drug.
Trial registration: The trial was registered with ClinicalTrials.gov (Study Number NCT01763645, date of registration 09/01/2013).
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Botrel TE, et al. Efficacy of bevacizumab (Bev) plus chemotherapy (CT) compared to CT alone in previously untreated locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): systematic review and meta-analysis. Lung Cancer. 2011;74(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2011.01.028. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Orlov SV, et al. Pharmacokinetics and safety of BCD-021, bevacizumab biosimilar candidate, compared to Avastin in patients. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(15_suppl):e13500. doi: 10.1200/jco.2014.32.15_suppl.e13500. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

