Multiple tracer dilution estimates of D- and 2-deoxy-D-glucose uptake by the heart
- PMID: 3510568
- PMCID: PMC3496757
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.1986.250.1.H29
Multiple tracer dilution estimates of D- and 2-deoxy-D-glucose uptake by the heart
Abstract
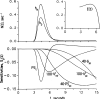
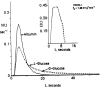
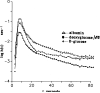
Permeability-surface area products of the capillary wall, PSc, and the myocyte sarcolemma, PSpc, for D-glucose and 2-deoxy-D-glucose were estimated via the multiple indicator-dilution technique in isolated blood-perfused dog and Tyrode-perfused rabbit hearts. Aortic bolus injections contained 131I-albumin (intravascular reference), two of three glucoses: L-glucose (an extracellular reference solute), D-glucose, and 2-deoxy-D-glucose. Outflow dilution curves were sampled for 1-2.5 min without recirculation. The long duration sampling allowed accurate evaluation of PSpc by fitting the dilution curves with a multiregional axially distributed capillary-interstitial fluid-cell model accounting for the heterogeneity of regional flows (measured using microspheres and total heart sectioning). With average blood flow of 1.3 ml . g-1 . min-1, in the dog hearts the PSc for D-glucose was 0.72 +/- 0.17 ml . g-1 . min-1 (mean +/- SD; n = 11), and PSpc was 0.57 +/- 0.15 ml . g-1 . min-1. In the rabbit hearts with perfusate flow of 2.0 ml . g-1 . min-1 (n = 6), PSc was 1.2 +/- 0.1 and PSpc was 0.4 +/- 0.1 ml . g-1 . min-1. PSc for 2-deoxy-D-glucose was about 4% higher than for D-glucose and L-glucose in both preparations. Relative to L-glucose, there was no measurable transendothelial transport of either dextroglucose, indicating that transcapillary transport was by passive diffusion, presumably via the clefts between cells. The technique allows repeated measurements of D-glucose uptake at intervals of a few minutes; it may therefore be used to assess changes in transport rates occurring over intervals of several minutes.
Figures

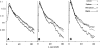
References
-
- Bassingthwaighte JB, Goresky CA. Handbook of Physiology. The Cardiovascular System. Microcirculation. Vol. 4. Am. Physiol. Soc.; Bethesda, MD: 1984. Modeling in the analysis of solute and water exchange in the microvasculature. pp. 549–626. sect. 2. chapt. 13.
-
- Bassingthwaighte JB, Lenhoff AM, Stephenson JL. A sliding-element algorithm for rapid solution of spatially distributed convection-permeation models (Abstract). Biophys. J. 1984;45:175a.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

