Social determinants of health and pediatric cancer survival: A systematic review
- PMID: 35107854
- PMCID: PMC8957569
- DOI: 10.1002/pbc.29546
Social determinants of health and pediatric cancer survival: A systematic review
Abstract
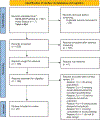
Despite treatment advancements and improved survival, approximately 1800 children in the United States will die of cancer annually. Survival may depend on nonclinical factors, such as economic stability, neighborhood and built environment, health and health care, social and community context, and education, otherwise known as social determinants of health (SDoH). Extant literature reviews have linked socioeconomic status (SES) and race to disparate outcomes; however, these are not inclusive of all SDoH. Thus, we conducted a systematic review on associations between SDoH and survival in pediatric cancer patients. Of the 854 identified studies, 25 were included in this review. In addition to SES, poverty and insurance coverage were associated with survival. More studies that include other SDoH, such as social and community factors, utilize prospective designs, and conduct analyses with more precise SDoH measures are needed.
Keywords: adolescents; cancer health disparities; childhood cancer; pediatrics; social determinants of health; survival.
© 2022 The Authors. Pediatric Blood & Cancer published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- ACCO. US Childhood Cancer Statistics. ACCO. Accessed February 23, 2021. https://www.acco.org/us-childhood-cancer-statistics/
-
- National Cancer Institute. Cancer in Children and Adolescents. National Cancer Institute; September 1, 2017. Accessed February 23, 2021. https://www.cancer.gov/types/childhood-cancers/child-adolescent-cancers-...
-
- Key statistics for childhood cancers. American Cancer Society; 2021. Accessed February 23, 2021. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/cancer-in-children/key-statistics.html
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical