Rare Autoinflammatory Diseases
- PMID: 35110074
- PMCID: PMC8867516
- DOI: 10.5152/TurkArchPediatr.2022.21303
Rare Autoinflammatory Diseases
Abstract
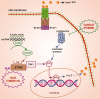
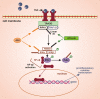
Systemic autoinflammatory diseases are disorders caused by dysregulation of the innate immune system leading to systemic inflammation. Since the first gene had been identified causing Familial Mediterranean Fever, the most common hereditary systemic autoinflammatory disease, advances in genomic techniques and awareness of the diseases have led to identifying more genes causing autoinflammatory conditions affecting different parts of the innate immune system. The aim of this review is to provide an update on some recently discovered autoinflammatory conditions and raise awareness for the clinicians. We focused on the actinopathies, interferonopathies, and NF-κB-mediated autoinflammatory diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
