Multiview motion tracking based on a cartesian robot to monitor Caenorhabditis elegans in standard Petri dishes
- PMID: 35110654
- PMCID: PMC8810772
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-05823-6
Multiview motion tracking based on a cartesian robot to monitor Caenorhabditis elegans in standard Petri dishes
Abstract
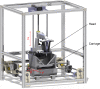
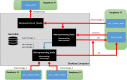
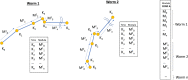
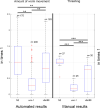
Data from manual healthspan assays of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) can be complex to quantify. The first attempts to quantify motor performance were done manually, using the so-called thrashing or body bends assay. Some laboratories have automated these approaches using methods that help substantially to quantify these characteristic movements in small well plates. Even so, it is sometimes difficult to find differences in motor behaviour between strains, and/or between treated vs untreated worms. For this reason, we present here a new automated method that increases the resolution flexibility, in order to capture more movement details in large standard Petri dishes, in such way that those movements are less restricted. This method is based on a Cartesian robot, which enables high-resolution images capture in standard Petri dishes. Several cameras mounted strategically on the robot and working with different fields of view, capture the required C. elegans visual information. We have performed a locomotion-based healthspan experiment with several mutant strains, and we have been able to detect statistically significant differences between two strains that show very similar movement patterns.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Authors reported a potential conflict of interest related to patent royalties of the multi-view robot device.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Rapid measurement of ageing by automated monitoring of movement of C. elegans populations.Geroscience. 2024 Apr;46(2):2281-2293. doi: 10.1007/s11357-023-00998-w. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Geroscience. 2024. PMID: 37940787 Free PMC article.
-
Active backlight for automating visual monitoring: An analysis of a lighting control technique for Caenorhabditis elegans cultured on standard Petri plates.PLoS One. 2019 Apr 16;14(4):e0215548. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215548. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30990857 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing motor-related phenotypes of Caenorhabditis elegans with the wide field-of-view nematode tracking platform.Nat Protoc. 2020 Jun;15(6):2071-2106. doi: 10.1038/s41596-020-0321-9. Epub 2020 May 20. Nat Protoc. 2020. PMID: 32433626
-
Strategies for automated analysis of C. elegans locomotion.Invert Neurosci. 2008 Sep;8(3):121-31. doi: 10.1007/s10158-008-0077-3. Epub 2008 Aug 8. Invert Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18688666 Review.
-
Automated imaging of C. elegans behavior.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;351:241-51. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-151-7:241. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16988438 Review.
Cited by
-
Track-A-Worm 2.0: A Software Suite for Quantifying Properties of C. elegans Locomotion, Bending, Sleep, and Action Potentials.eNeuro. 2025 Aug 27;12(8):ENEURO.0224-25.2025. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0224-25.2025. Print 2025 Aug. eNeuro. 2025. PMID: 40866299 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of a C. elegans lifespan prediction method based on a bimodal neural network and uncertainty estimation.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Dec 29;21:655-664. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.12.033. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 36659931 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic segmentation of Caenorhabditis elegans skeletons in worm aggregations using improved U-Net in low-resolution image sequences.Heliyon. 2023 Mar 22;9(4):e14715. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14715. eCollection 2023 Apr. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37025880 Free PMC article.
-
Track-A-Worm 2.0: A Software Suite for Quantifying Properties of C. elegans Locomotion, Bending, Sleep, and Action Potentials.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 15:2024.09.12.612524. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.12.612524. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39314462 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Automation of Caenorhabditis elegans lifespan assay using a simplified domain synthetic image-based neural network training strategy.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023 Oct 10;21:5049-5065. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.10.007. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 37867965 Free PMC article.

