Exhausted and Apoptotic BALF T Cells in Proinflammatory Airway Milieu at Acute Phase of Severe Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Pneumonia in Children
- PMID: 35111152
- PMCID: PMC8801936
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.760488
Exhausted and Apoptotic BALF T Cells in Proinflammatory Airway Milieu at Acute Phase of Severe Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Pneumonia in Children
Abstract
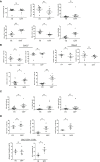
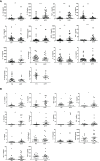
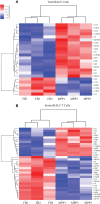
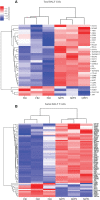
Severe mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (MPP) in children presents with serious clinical complications. Without proper and prompt intervention, it could lead to deadly consequences. Dynamics of the inflammatory airway milieu and activation status of immune cells were believed to be the hallmark of the pathogenesis and progress of the disease. In this study, by employing the T-cell sorting and mRNA microarray, we were able to define the main feature of the chemokine/cytokine expression and the unique characteristics of T cells in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) from severe MPP patients at acute phase. Our study for the first time delineated the molecular changes in isolated BALF T cells in severe MPP children with respect to the cytokine/chemokine expression, cell activation, exhaustion, and apoptosis. By comparing the BALF aqueous expression of cytokines/chemokines with that in sorted T cells, our data give a preliminary clue capable of finishing out the possible cell source of the proinflammatory cytokines/chemokines from the BALF mixture. Meanwhile, our data provide a distinctively pellucid expression profile particularly belonging to the isolated BALF T cells demonstrating that in the inflammatory airway, overactivated T cells were exhausted and on the verge of apoptotic progress.
Keywords: T cells; bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF); cell exhaustion; children; mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia (MPP); proinflammatory milieu.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Liu, Zheng, Kang, Wang, Mou, Zhang, Jiao, Zhao and Gui.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Koh YY, Park Y, Lee HJ, Kim CK. Levels of Interleukin-2, Interferon-Gamma, and Interleukin-4 in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid From Patients With Mycoplasma Pneumonia: Implication of Tendency Toward Increased Immunoglobulin E Production. Pediatrics (2001) 107(3):E39. doi: 10.1542/peds.107.3.e39 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

