G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 as Novel Therapeutic Target in Fibrotic Diseases
- PMID: 35111168
- PMCID: PMC8801426
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.822345
G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 as Novel Therapeutic Target in Fibrotic Diseases
Abstract
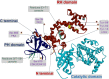
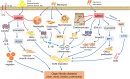
G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2), an important subtype of GRKs, specifically phosphorylates agonist-activated G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Besides, current research confirms that it participates in multiple regulation of diverse cells via a non-phosphorylated pathway, including interacting with various non-receptor substrates and binding partners. Fibrosis is a common pathophysiological phenomenon in the repair process of many tissues due to various pathogenic factors such as inflammation, injury, drugs, etc. The characteristics of fibrosis are the activation of fibroblasts leading to myofibroblast proliferation and differentiation, subsequent aggerate excessive deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM). Then, a positive feedback loop is occurred between tissue stiffness caused by ECM and fibroblasts, ultimately resulting in distortion of organ architecture and function. At present, GRK2, which has been described as a multifunctional protein, regulates copious signaling pathways under pathophysiological conditions correlated with fibrotic diseases. Along with GRK2-mediated regulation, there are diverse effects on the growth and apoptosis of different cells, inflammatory response and deposition of ECM, which are essential in organ fibrosis progression. This review is to highlight the relationship between GRK2 and fibrotic diseases based on recent research. It is becoming more convincing that GRK2 could be considered as a potential therapeutic target in many fibrotic diseases.
Keywords: ECM - extracellular matrix; G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2); G protein-coupled receptors; fibrosis; phosphorylation.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Shan, Li, Chen, Qi, Zhang, Wang, Zhang, Wei and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Antagonistic Roles of GRK2 and GRK5 in Cardiac Aldosterone Signaling Reveal GRK5-Mediated Cardioprotection via Mineralocorticoid Receptor Inhibition.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 20;21(8):2868. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082868. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32326036 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory effects of GRK2 on GPCRs and non-GPCRs and possible use as a drug target (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2016 Oct;38(4):987-94. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2720. Epub 2016 Aug 29. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27573285 Review.
-
GRK2-dependent desensitization downstream of G proteins.J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2008;28(1-2):59-70. doi: 10.1080/10799890801941939. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2008. PMID: 18437630 Review.
-
[Molecular basis for the potential role of GRK2 in pathological disorders].Nihon Rinsho. 2016 Oct;74(10):1761-1768. Nihon Rinsho. 2016. PMID: 30551294 Japanese.
-
GRK2: multiple roles beyond G protein-coupled receptor desensitization.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2012 Mar;33(3):154-64. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2011.12.003. Epub 2012 Jan 23. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22277298 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Uncovering conserved networks and global conformational changes in G protein-coupled receptor kinases.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024 Sep 28;23:3445-3453. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2024.09.014. eCollection 2024 Dec. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 39403406 Free PMC article.
-
Cardioprotective Effects of the GRK2 Inhibitor Paroxetine on Isoproterenol-Induced Cardiac Remodeling by Modulating NF-κB Mediated Prohypertrophic and Profibrotic Gene Expression.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 8;24(24):17270. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417270. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139099 Free PMC article.
-
Paroxetine attenuated liver fibrosis in liver of bile duct ligated rats: role of P2X4 purinoreceptor.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 May 23. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04278-6. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40407866
-
N-terminal domain of CTRP9 promotes cardiac fibroblast activation in myocardial infarction via Rap1/Mek/Erk pathway.J Transl Med. 2025 Mar 10;23(1):300. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06274-z. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40065407 Free PMC article.
-
The Sympathetic Nervous System in Hypertensive Heart Failure with Preserved LVEF.J Clin Med. 2023 Oct 12;12(20):6486. doi: 10.3390/jcm12206486. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37892623 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

