Evaluation of Serum MicroRNAs (miR-9-5p, miR-17-5p, and miR-148a-3p) as Potential Biomarkers of Breast Cancer
- PMID: 35111850
- PMCID: PMC8803421
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/9961412
Evaluation of Serum MicroRNAs (miR-9-5p, miR-17-5p, and miR-148a-3p) as Potential Biomarkers of Breast Cancer
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play important roles in the initiation and progression of cancers. The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the use of serum miRNA biomarkers in the early diagnosis of breast cancer.
Methods: The expression levels of miR-9-5p, miR-17-5p, and miR-148a-3p were analyzed by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction in 49 patients with newly diagnosed breast cancer and 49 healthy controls. The associations between miR-9-5p, miR-17-5p, and miR-148a-3p levels and clinicopathological parameters were also analyzed. Regression analysis and sensitivity and specificity analyses were used to determine the diagnostic efficacy of the miRNAs.
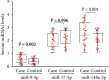
Results: Serum levels of miR-9-5p and miR-148a-3p were significantly higher in breast cancer patients than in healthy controls (both P < 0.05), but miR-17-5p levels were not different between the two groups (P = 0.996). Serum miR-9-5p levels were markedly higher in patients with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2- (HER2-) positive breast cancer than in those with HER2-negative breast cancer (P = 0.049). Serum levels of miR-9-5p and miR-148a-3p were positively correlated with the presence of breast cancer, and both miRNAs had high sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of breast cancer.
Conclusions: These findings provide evidence that serum miR-9-5p and miR-148a-3p levels may be used as noninvasive biological markers for the clinical diagnosis of breast cancer.
Copyright © 2022 Xiaoqin Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous