Single Cell RNA Sequencing Identifies a Unique Inflammatory Macrophage Subset as a Druggable Target for Alleviating Acute Kidney Injury
- PMID: 35112806
- PMCID: PMC9036000
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202103675
Single Cell RNA Sequencing Identifies a Unique Inflammatory Macrophage Subset as a Druggable Target for Alleviating Acute Kidney Injury
Abstract
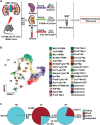
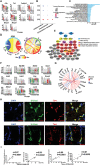
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a complex clinical disorder associated with poor outcomes. Targeted regulation of the degree of inflammation has been a potential strategy for AKI management. Macrophages are the main effector cells of kidney inflammation. However, macrophage heterogeneity in ischemia reperfusion injury induced AKI (IRI-AKI) remains unclear. Using single-cell RNA sequencing of the mononuclear phagocytic system in the murine IRI model, the authors demonstrate the complementary roles of kidney resident macrophages (KRMs) and monocyte-derived infiltrated macrophages (IMs) in modulating tissue inflammation and promoting tissue repair. A unique population of S100a9hi Ly6chi IMs is identified as an early responder to AKI, mediating the initiation and amplification of kidney inflammation. Kidney infiltration of S100A8/A9+ macrophages and the relevance of renal S100A8/A9 to tissue injury is confirmed in human AKI. Targeting the S100a8/a9 signaling with small-molecule inhibitors exhibits renal protective effects represented by improved renal function and reduced mortality in bilateral IRI model, and decreased inflammatory response, ameliorated kidney injury, and improved long-term outcome with decreased renal fibrosis in the unilateral IRI model. The findings support S100A8/A9 blockade as a feasible and clinically relevant therapy potentially waiting for translation in human AKI.
Keywords: S100a9; acute kidney injury; inflammation; macrophage; single-cell RNA-seq; therapeutic target.
© 2022 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 91742205/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81625004/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82130021/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- BJJWZYJH01201910001006/the Beijing Young Scientists Program
- Peking University Clinical Scientist Program by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
