Prevalence and Durability of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies Among Unvaccinated US Adults by History of COVID-19
- PMID: 35113143
- PMCID: PMC8814952
- DOI: 10.1001/jama.2022.1393
Prevalence and Durability of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies Among Unvaccinated US Adults by History of COVID-19
Abstract
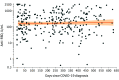
This study uses serologic testing to characterize natural immunity and the long-term durability of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies among unvaccinated US adults by history of COVID-19 infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Clinical Protection During the First Omicron Wave in Unvaccinated, Convalescent US Adults.JAMA. 2022 Jul 12;328(2):212. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.10332. JAMA. 2022. PMID: 35819428 No abstract available.
References
-
- USAFacts . Secondary US coronavirus vaccine tracker 2021. Accessed December 28, 2021. https://usafacts.org/issues/coronavirus/
-
- Gilbert PB, Montefiori DC, McDermott AB, et al. ; Immune Assays Team; Moderna Inc Team; Coronavirus Vaccine Prevention Network (CoVPN)/Coronavirus Efficacy (COVE) Team; US Government (USG)/CoVPN Biostatistics Team . Immune correlates analysis of the mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccine efficacy clinical trial. Science. 2022;375(6576):43-50. doi:10.1126/science.abm3425 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

