On-line Electrode Dissolution Monitoring during Organic Electrosynthesis: Direct Evidence of Electrode Dissolution during Kolbe Electrolysis
- PMID: 35114080
- PMCID: PMC9304240
- DOI: 10.1002/cssc.202102228
On-line Electrode Dissolution Monitoring during Organic Electrosynthesis: Direct Evidence of Electrode Dissolution during Kolbe Electrolysis
Abstract
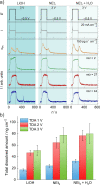
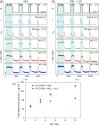
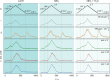
Electrode dissolution was monitored in real-time during Kolbe electrolysis along with the characteristic products. The fast determination of appropriate reaction conditions in electro-organic chemistry enables the minimization of electrode degradation while keeping an eye on the optimal formation rate and distribution of products. Herein, essential parameters influencing the dissolution of the electrode material platinum in a Kolbe electrolysis were pinpointed. The formation of reaction products and soluble platinum species were monitored during potentiodynamic and potentiostatic experiments using an electroanalytical flow cell coupled to two different mass spectrometers. The approach opens new vistas in the field of electro-organic chemistry because it enables precise and quick quantification of dissolved metals during electrosynthesis, also involving electrode materials other than platinum. Furthermore, it draws attention to the vital topic of electrode stability in electro-organic synthesis, which becomes increasingly important for the implementation of green chemical processes utilizing renewable energy.
Keywords: Kolbe electrolysis; Pt dissolution; electrochemistry; electrode stability; online electrochemical mass spectrometer.
© 2022 The Authors. ChemSusChem published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- None
-
- Frontana-Uribe B. A., Little R. D., Ibanez J. G., Palma A., Vasquez-Medrano R., Green Chem. 2010, 12, 2099–2119;
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

