COVID-19 Detection Based on Lung Ct Scan Using Deep Learning Techniques
- PMID: 35116074
- PMCID: PMC8805449
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/7672196
COVID-19 Detection Based on Lung Ct Scan Using Deep Learning Techniques
Retraction in
-
Retracted: COVID-19 Detection Based on Lung Ct Scan Using Deep Learning Techniques.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Oct 11;2023:9840132. doi: 10.1155/2023/9840132. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 37867554 Free PMC article.
Abstract
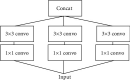
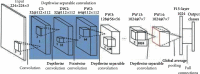
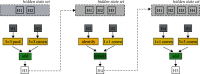
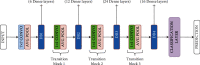
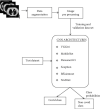
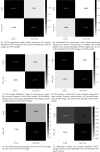
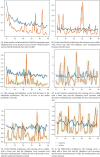
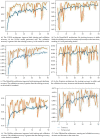
SARS-CoV-2 is a novel virus, responsible for causing the COVID-19 pandemic that has emerged as a pandemic in recent years. Humans are becoming infected with the virus. In 2019, the city of Wuhan reported the first-ever incidence of COVID-19. COVID-19 infected people have symptoms that are related to pneumonia, and the virus affects the body's respiratory organs, making breathing difficult. A real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) kit is used to diagnose the disease. Due to a shortage of kits, suspected patients cannot be treated promptly, resulting in disease spread. To develop an alternative, radiologists looked at the changes in radiological imaging, like CT scans, that produce comprehensive pictures of the body of excellent quality. The suspected patient's computed tomography (CT) scan is used to distinguish between a healthy individual and a COVID-19 patient using deep learning algorithms. A lot of deep learning methods have been proposed for COVID-19. The proposed work utilizes CNN architectures like VGG16, DeseNet121, MobileNet, NASNet, Xception, and EfficientNet. The dataset contains 3873 total CT scan images with "COVID" and "Non-COVID." The dataset is divided into train, test, and validation. Accuracies obtained for VGG16 are 97.68%, DenseNet121 is 97.53%, MobileNet is 96.38%, NASNet is 89.51%, Xception is 92.47%, and EfficientNet is 80.19%, respectively. From the obtained analysis, the results show that the VGG16 architecture gives better accuracy compared to other architectures.
Copyright © 2022 S. V. Kogilavani et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Kumar S., Maheshwari V., Prabhu J., et al. Social economic impact of COVID-19 outbreak in India. International Journal of Pervasive Computing and Communications . 2020;16(4):309–319.
-
- Priya K. B., Rajendran P., Kumar S., et al. Pediatric and geriatric immunity network mobile computational model for COVID-19. International Journal of Pervasive Computing and Communications . 2020;16(4):321–330. doi: 10.1108/IJPCC-06-2020-0054. - DOI
-
- Mathivanan S. K., Jayagopal P., Ahmed S., et al. Adoption of e-learning during lockdown in India. International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management . 2021:1–10. doi: 10.1007/s13198-021-01072-4. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

