Identification of CDK1 as a candidate marker in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by integrated bioinformatics analysis
- PMID: 35116276
- PMCID: PMC8797450
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-20-2945
Identification of CDK1 as a candidate marker in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma by integrated bioinformatics analysis
Abstract
Background: Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) is a relatively common cancer that accounts for nearly 50% of non-melanoma skin cancer cases. However, the genotypes that are linked with poor prognosis and/or high relapse rates and pathogenic mechanisms of cSCC are not fully understood. To address these points, three gene expression datasets were analyzed to identify candidate biomarker genes in cSCC.
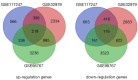
Methods: The GSE117247, GSE32979, and GSE98767 datasets comprising a total of 32 cSCC samples and 31 normal skin tissue samples were obtained from the National Center for Biotechnology Information Gene Expression Omnibus database. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified and underwent pathway enrichment analyses with the Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG). A putative DEG protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was also established that included hub genes. The expression of CDK1, MAD2L1, BUB1 ans CDC20 were examined in the study.
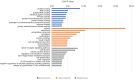
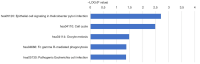
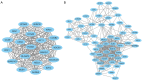
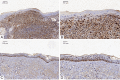
Results: A total of 335 genes were identified, encompassing 219 found to be upregulated and 116 genes that were downregulated in cSCC, compared to normal tissue. Enriched functions of these DEGs were associated with Ephrin receptor signaling and cell division; cytosol, membrane, and extracellular exosomes; ATP-, poly(A) RNA-, and identical protein binding. We also established a PPI network comprising 332 nodes and identified KIF2C, CDC42, AURKA, MAD2L1, MYC, CDK1, FEN1, H2AFZ, BUB1, BUB1B, CKS2, CDC20, CCT2, ACTR2, ACTB, MAPK14, and HDAC1 as candidate hub genes. The expression of CDK1 are significantly higher in the cSCC tissues than that in normal skin.
Conclusions: The DEGs identified in this study are potential therapeutic targets and biomarkers for cSCC. CDK1 is a gene closely related to the occurrence and development of cSCC, which may play an important role. Bioinformatics analysis shows that it is involved in the important pathway of the pathogenesis of cSCC, and may be recognized and applied as a new biomarker in the future diagnosis and treatment of cSCC.
Keywords: Cluster analysis; carcinoma; critical pathways; genetic association studies; squamous cell.
2021 Translational Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tcr-20-2945). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
