COL6A6 inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer through the JAK signalling pathway
- PMID: 35116307
- PMCID: PMC8798920
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-21-2002
COL6A6 inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer through the JAK signalling pathway
Abstract
Background: Collagen type VI alpha 6 chain (COL6A6) plays a vital role in maintaining cell structural integrity and regulating cell function. It has been proven to be a tumor suppressor gene and molecular therapeutic target. However, the mechanism of COL6A6 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has not been elucidated. The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between COL6A6 and NSCLC.
Methods: We analyzed the expression of COL6A6 in NSCLC using public databases and verified the findings in NSCLC tissues and cells. The protein expression of COL6A6 was evaluated by Western blot. The CCK8 and Transwell assays were used to assess the invasion ability of NSCLC cells after COL6A6 knockdown. At the same time, we discussed the role of the JAK signalling pathway that may be related to COL6A6.
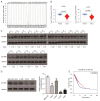
Results: Bioinformatics analysis showed that COL6A6 expression was downregulated in NSCLC, and its high expression was associated with a better prognosis of NSCLC. In vitro, the expression of COL6A6 in NSCLC tissues was significantly lower than that in adjacent tissues. Furthermore, COL6A6 knockout accelerated the proliferation, invasion, and migration of NSCLC cells and activated the JAK signalling pathway.
Conclusions: Our study illustrates that COL6A6 is a tumor suppressor gene in NSCLC and is involved in NSCLC tumorigenesis by regulating the JAK signalling pathway. Therefore, COL6A6 holds promise as a molecular therapeutic target for NSCLC.
Keywords: Collagen type VI alpha 6 chain (COL6A6); JAK signalling; invasion; non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); proliferation.
2021 Translational Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tcr-21-2002). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
