A systematic review and meta-analysis of indirect comparison between miRNA and ctDNA in diagnosis of epithelial ovarian cancer
- PMID: 35116384
- PMCID: PMC8799085
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-21-2609
A systematic review and meta-analysis of indirect comparison between miRNA and ctDNA in diagnosis of epithelial ovarian cancer
Retraction in
-
Retraction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of indirect comparison between miRNA and ctDNA in diagnosis of epithelial ovarian cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2022 Apr;11(4):980. doi: 10.21037/tcr-22-862. Transl Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35571663 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: To evaluate the clinical value of microRNA (miR) and circulating tumor RNA (ctDNA) in the diagnosis of epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) by meta-analysis and indirect comparison based on common reference criteria.
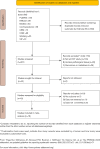
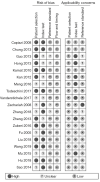
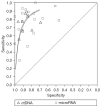
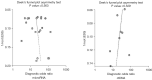
Methods: The PubMed, EMBASE, MEDLINE, Cochrane Library, Chinese biology medicine (CBM), China national knowledge infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang, and Chinese Weipu (VIP) databases were searched by computer. The retrieval time limit was from the date of establishment of the database to September 2020. Two researchers independently screened the literature and extracted the basic data according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria formulated in advance, and evaluated the literature quality according to the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy research (quadas-2). The Meta disc 1.4 and Stata 12.0 software programs were used for meta-analysis to calculate the combined sensitivity, combined specificity, combined positive likelihood ratio, combined negative likelihood ratio and combined diagnostic odds ratio (DOR). The summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) curve was drawn using Revman 5.3 software, and the stability of the results was evaluated by sensitivity analysis. The publication bias was evaluated by Deek's funnel asymmetric test. The relative diagnostic odds ratio (RDOR) results of indirect comparison between microRNA and ctDNA were obtained using R software.
Results: Nineteen articles were included, including a total of 1,351 EOC patients and 1,194 controls. The heterogeneity test showed that there was obvious heterogeneity caused by non-threshold effect. The random effects model was used for meta-analysis of microRNA in the diagnosis of EOC. The results showed that there was no significant difference between microRNA and ctDNA in the accuracy of EOC diagnosis. The asymmetric test of Deek's funnel chart showed that there was no significant publication bias.
Discussion: There are some limitations in this study, there is no blind diagnostic test, and the intensity of indirect comparison evidence is lower than that of direct comparison evidence. The accuracy of diagnostic tests and the imperfection of mesh meta-analysis statistical methods. MicroRNA and ctDNA have similar clinical diagnostic value for EOC.
Keywords: Epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC); ctDNA; indirect comparison; meta-analysis; microRNA.
2021 Translational Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Both authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tcr-21-2609). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
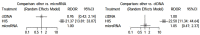
Similar articles
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism.BMC Med Imaging. 2025 Mar 20;25(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12880-025-01629-w. BMC Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40114100 Free PMC article.
-
[Meta-analysis on the diagnostic value of laser Doppler imaging for burn depth].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2017 May 20;33(5):301-308. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2017.05.009. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28651422 Chinese.
-
[Diagnostic accuracy of artery peak velocity variation measured by bedside real-time ultrasound for prediction of fluid responsiveness: a Meta-analysis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Jan;32(1):99-105. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20191226-00018. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 32148240 Chinese.
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic value of computed tomography angiography for severe internal carotid artery stenosis.BMC Med Imaging. 2024 Aug 14;24(1):215. doi: 10.1186/s12880-024-01390-6. BMC Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39143526 Free PMC article.
-
An indirect comparison of automated indirect immunofluorescence vs automated solid-phase immunoassays for antinuclear antibody detection: A meta-analysis and adjusted indirect comparison of diagnostic test accuracy.Int J Rheum Dis. 2022 Sep;25(9):991-1002. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.14369. Epub 2022 Jun 21. Int J Rheum Dis. 2022. PMID: 35726725
Cited by
-
Meta-analysis of the diagnostic value of 18F-FDG PET/CT in the recurrence of epithelial ovarian cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Nov 7;12:1003465. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1003465. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36419900 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of PARP Inhibitor Combined with Bevacizumab on Platinum-Resistant Recurrent Ovarian Epithelial Carcinoma.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Jun 10;2022:4600145. doi: 10.1155/2022/4600145. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Jun 28;2023:9823491. doi: 10.1155/2023/9823491. PMID: 35720032 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The frequency and characterization of ovarian metastasis from nonovarian cancers using 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT.BJR Open. 2025 Mar 18;7(1):tzaf004. doi: 10.1093/bjro/tzaf004. eCollection 2025 Jan. BJR Open. 2025. PMID: 40161429 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
