Up-regulation of SOCS4 promotes cell proliferation and migration in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 35116557
- PMCID: PMC8798805
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-21-700
Up-regulation of SOCS4 promotes cell proliferation and migration in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Suppressors of cytokine signaling family member 4 (SOCS4) was shown to serve critical and multifaceted roles in the progression of numerous cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma, thyroid cancer, breast cancer, and lung adenocarcinoma. While, the expression and the roles of SOCS4 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) remain elusive. The current study is aimed to investigate the expression pattern and functions of SOCS4 in ESCC.
Methods: The relationship between SOCS4 and the clinicopathological features of ESCC was analyzed. SOCS4 expression in ESCC tissues was measured by western blot, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), and immunohistochemical (IHC) staining. The roles of SOCS4 in modulating ESCC cell behaviors were examined using a series of assays, including cell proliferation assay, cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay, cell cycle analysis, and wound-healing assay.
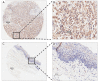
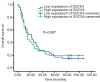
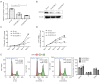
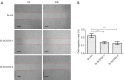
Results: In human ESCC tissues, SOCS4 expression was up-regulated and correlated with tumor size and lymph node metastasis, however was not correlated with the overall survival (OS) of patients. SOCS4 silencing in ESCC cells resulted in the suppression of cell growth, which was related to the cell cycle. SOCS4 knockdown also inhibited nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling and decreased the migratory potential of ESCC cells.
Conclusions: These findings revealed that increased expression of SOCS4 in ESCC may promote the progression, proliferation, and migration by NF-κB signaling. Inhibition of SOCS4 may be a promising therapeutic strategy for ESCC.
Keywords: NF-κB; Suppressors of cytokine signaling family member 4 (SOCS4); esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC); migration; proliferation.
2021 Translational Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tcr-21-700). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Long noncoding RNA H19 is up-regulated in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and promotes cell proliferation and metastasis.Dis Esophagus. 2017 Jan 1;30(1):1-9. doi: 10.1111/dote.12481. Dis Esophagus. 2017. PMID: 27247022
-
MicroRNA-429 inhibits the proliferation and migration of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells by targeting RAB23 through the NF-κB pathway.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Feb;24(3):1202-1210. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202002_20172. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32096149
-
High MLL2 expression predicts poor prognosis and promotes tumor progression by inducing EMT in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018 Jun;144(6):1025-1035. doi: 10.1007/s00432-018-2625-5. Epub 2018 Mar 12. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29532228 Free PMC article.
-
BRCA1-Associated Protein Increases Invasiveness of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Gastroenterology. 2017 Nov;153(5):1304-1319.e5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.07.042. Epub 2017 Aug 2. Gastroenterology. 2017. PMID: 28780075
-
Knockdown of DDX46 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells.Oncol Rep. 2016 Jul;36(1):223-30. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.4803. Epub 2016 May 11. Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27176873
Cited by
-
MiR-568-5p, the key regulator of suppressor of cytokine signaling 4 (SOCS4) in the coronary artery disease.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2025 Apr 22;24(1):106. doi: 10.1007/s40200-025-01619-3. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2025. PMID: 40276596
-
Bufalin suppresses esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression by activating the PIAS3/STAT3 signaling pathway.J Thorac Dis. 2023 Apr 28;15(4):2141-2160. doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-486. Epub 2023 Apr 25. J Thorac Dis. 2023. PMID: 37197494 Free PMC article.
-
The Neglected Suppressor of Cytokine Signalling (SOCS): SOCS4-7.Inflammation. 2025 Aug;48(4):1607-1623. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02163-7. Epub 2024 Oct 26. Inflammation. 2025. PMID: 39460806 Review.
-
SPP1 promotes tumor progression in esophageal carcinoma by activating focal adhesion pathway.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Jun 30;15(3):818-828. doi: 10.21037/jgo-24-302. Epub 2024 Jun 27. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38989403 Free PMC article.
-
Expression Characteristics, Immune Signature, and Prognostic Value of the SOCS Family Identified by Multiomics Integrative Analysis in Liver Cancer.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024 Sep;7(9):e2161. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.2161. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 39307915 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
