Prognostic values of platelet-associated indicators in advanced breast cancer
- PMID: 35116875
- PMCID: PMC8798875
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr.2019.07.28
Prognostic values of platelet-associated indicators in advanced breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in the female population. Platelet-related indicators can be used as prognostic markers of cancers. The present study investigated the potential values of platelet count (PLT), plateletcrit (PCT), mean platelet volume (MPV), platelet distribution width (PDW), and platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) in the prognosis of advanced breast cancer (ABC).
Methods: This retrospective study recruited 94 locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer cases who had histologic and cytologic evidence. The patients were divided into two groups according to the median baseline values of PLT, PCT, MPV, PDW, and PLR. To evaluate the individual value changes after treatment, we introduced the concept of post/pre-treatment ratio (≤1 indicated value was not increased after treatment, while >1 suggested increased value). Responses to chemotherapy, including partial response (PR), stable disease (SD), and progressive disease (PD), were recorded. Kaplan-Meier curves were constructed to show overall survival (OS). Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analysis models were employed to identify the independent risk factors.
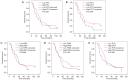
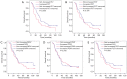
Results: A lower baseline PCT level was correlated with a better OS. A lower baseline PLT level and a higher baseline PDW level were related to better chemotherapeutic efficacy of breast cancer patients. Univariate analysis and multivariate analysis both revealed that a higher baseline PCT level was an independent prognostic factor for OS.
Conclusions: PCT level may be a potential prognosis factor for ABC.
Keywords: Breast cancer; platelet count (PLT); plateletcrit (PCT); prognosis.
2019 Translational Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tcr.2019.07.28). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic evaluation of resectable colorectal cancer using platelet-associated indicators.Oncol Lett. 2019 Jul;18(1):571-580. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10388. Epub 2019 May 21. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31289529 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Values of Platelet-Associated Indicators in Resectable Lung Cancers.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Jan 1;18:1533033819837261. doi: 10.1177/1533033819837261. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 30871415 Free PMC article.
-
Association between platelet indices and the severity of the disease and mortality in patients with COVID-19.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Nov;25(21):6731-6740. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202111_27118. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34787878
-
Prognostic Values of Platelet-Associated Indicators in Resectable Cervical Cancer.Dose Response. 2019 Sep 8;17(3):1559325819874199. doi: 10.1177/1559325819874199. eCollection 2019 Jul-Sep. Dose Response. 2019. PMID: 31523206 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value of Evaluating Platelet Role, Count and Indices in Laboratory Diagnosis of Different Types of Solid Malignancies.Pak J Biol Sci. 2022 Jan;25(2):100-105. doi: 10.3923/pjbs.2022.100.105. Pak J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35233997 Review.
Cited by
-
Total RNA nonlinear polarization: towards facile early diagnosis of breast cancer.RSC Adv. 2021 Oct 11;11(53):33319-33325. doi: 10.1039/d1ra05599b. eCollection 2021 Oct 8. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35497529 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid biopsy in breast cancer: Redefining precision medicine.J Liq Biopsy. 2025 Jul 16;9:100312. doi: 10.1016/j.jlb.2025.100312. eCollection 2025 Sep. J Liq Biopsy. 2025. PMID: 40740670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plateletcrit is predictive of clinical outcome and prognosis for early-stage breast cancer: A retrospective cohort study based on propensity score matching.Cancer Med. 2024 Jan;13(2):e6944. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6944. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38348939 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative platelet distribution width predicts bone metastasis in patients with breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2024 Aug 29;24(1):1066. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12837-y. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39210343 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Inflammatory Protein Ratio (IPR) as an Inflammation-Based Biomarker for Cancer Diagnosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 5;26(9):4375. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094375. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362613 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
