Bioinformatics analysis to reveal key biomarkers for early and late hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 35117777
- PMCID: PMC8798999
- DOI: 10.21037/tcr-19-2238
Bioinformatics analysis to reveal key biomarkers for early and late hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to find the long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and mRNAs acting as biomarker of early and late hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Methods: The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) dataset was used to identify shared differentially expressed lncRNAs (DElncRNAs) and mRNAs (DEmRNAs) between early and late HCC and normal tissue. Functional annotation and protein-protein interaction network of shared DEmRNAs were performed. Furthermore, DElncRNAs-DEmRNAs co-expression network of early and late HCC were also performed. The expression of selected candidate genes were validated by the quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR).
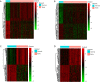
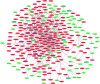
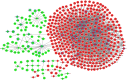
Results: A total of 1,201 shared DEmRNAs and 162 shared DElncRNAs were identified in both early and late HCC compared with normal controls. Cell cycle, p53 signaling pathway, retinol metabolism and metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 were four significantly enriched pathways. Base on the protein-protein interaction network, CDK1, AURKA, CDC20, PLK1, AURKB, HIST1H2BG, BUB1B, CCNA2, CCNB1 and CDT1 were key protein. CTD-2510F5.4 and HAND2-AS1 were hub lncRNAs in both early and late HCC. Overall, the confirmation results of qRT-PCR were generally consistent with our integrated analysis.
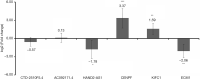
Conclusions: A total of 4 DEmRNAs (CDK1, KIFC1, CENPF and ECM1) and 2 DElncRNAs (CTD-2510F5.4 and HAND2-AS1) were identified as key biomarkers for HCC. This study may contribute to reveal the pathogenesis of early and late HCC and provide new and accurate therapeutic targets for HCC.
Keywords: DElncRNA-DEmRNA co-expression; Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); differentially expressed lncRNAs (DElncRNAs); differentially expressed mRNAs (DEmRNAs).
2020 Translational Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tcr-19-2238). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comprehensive analysis of key genes, microRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma.FEBS Open Bio. 2018 Jul 31;8(9):1424-1436. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12483. eCollection 2018 Sep. FEBS Open Bio. 2018. PMID: 30186744 Free PMC article.
-
Screening key lncRNAs for human rectal adenocarcinoma based on lncRNA-mRNA functional synergistic network.Cancer Med. 2019 Jul;8(8):3875-3891. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2236. Epub 2019 May 22. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 31116002 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of long noncoding RNAs biomarkers in patients with hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Biomark. 2018;23(1):95-106. doi: 10.3233/CBM-181424. Cancer Biomark. 2018. PMID: 29991128
-
Screening of tumor grade-related mRNAs and lncRNAs for Esophagus Squamous Cell Carcinoma.J Clin Lab Anal. 2021 Jun;35(6):e23797. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23797. Epub 2021 May 7. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021. PMID: 33960436 Free PMC article.
-
Reconstruction and Analysis of the Differentially Expressed IncRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network Based on Competitive Endogenous RNA in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019;29(6):539-549. doi: 10.1615/CritRevEukaryotGeneExpr.2019028740. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2019. PMID: 32422009 Review.
Cited by
-
Identifying potential signatures of immune cells in hepatocellular carcinoma using integrative bioinformatics approaches and machine-learning strategies.Immunol Res. 2025 Feb 4;73(1):46. doi: 10.1007/s12026-024-09585-3. Immunol Res. 2025. PMID: 39904830
-
Recent updates of centromere proteins in hepatocellular carcinoma: a review.Infect Agent Cancer. 2025 Feb 6;20(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s13027-024-00630-2. Infect Agent Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39915786 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
