Mass to voltage ratio index predicts mortality following TAVI
- PMID: 35119184
- PMCID: PMC9544118
- DOI: 10.1002/ccd.30117
Mass to voltage ratio index predicts mortality following TAVI
Abstract
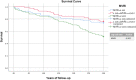
Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) is commonly performed in elderly patients with aortic stenosis. Better methods of risk stratification are needed in this population with high morbidity. There is a relatively high incidence of cardiac amyloidosis in this population and high LV mass index (LVMI) to QRS voltage may help identify patients with worse prognosis following TAVI. This retrospective study enrolled consecutive patients who underwent TAVI in our institution between the years 2008-2019. Mass voltage ratio index (MVRi) was calculated as the ratio of LV mass index on echocardiogram to voltage using the Sokolow-Lyon criteria on 12 lead ECG performed within 3 months before the intervention. Two hundred and fifty-one patients (mean age 80.8 years, 49% men) were enrolled. One hundred and sixty-eight (67%) patients were alive at 3 years follow up. MVRi was a statistically significant predictor of 3 year mortality (p < 0.005). Patients were divided categorically into tertiles based on MVRi score; the "high" group had significantly higher 3-year mortality (p < 0.001). In the multivariate model only Euroscore (p < 0.009) and MVRi (p < 0.011; OR: 2.32; CI: 1.15-4.964) were statistically significant predictors of mortality. The "high" group had a significantly lower survival rate after 3 years follow up on Kaplan-Meier analysis (p < 0.001). Our findings suggest that MVRi is a strong, independent predictor of increased post-TAVI mortality. This may be a simple clinical tool to assist in the assessment of patients prior to before TAVI.
Keywords: echocardiography; electrocardiography; transcatheter aortic valve replacement.
© 2022 The Authors. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Eveborn GW, Schirmer H, Heggelund G, Lunde P, Rasmussen K. The evolving epidemiology of valvular aortic stenosis. The Tromsø Study. Heart. 2013;99(6):396‐400. - PubMed
-
- Osnabrugge RLJ, Mylotte D, Head SJ, et al. Aortic stenosis in the elderly: disease prevalence and number of candidates for transcatheter aortic valve replacement: a meta‐analysis and modeling study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(11):1002‐1012. - PubMed
-
- Siontis GCM, Praz F, Pilgrim T, et al. Transcatheter aortic valve implantation vs. surgical aortic valve replacement for treatment of severe aortic stenosis: a meta‐analysis of randomized trials. Eur Heart J. 2016;37(47):3503‐3512. - PubMed
-
- Rodes‐Cabau J, Webb JG, Cheung A, et al. Long‐term outcomes after transcatheter aortic valve implantation: insights on prognostic factors and valve durability from the Canadian Multicenter Experience. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;60(19):1864‐1875. - PubMed
-
- Moat NE, Ludman P, De Belder MA, et al. Long‐term outcomes after transcatheter aortic valve implantation in high‐risk patients with severe aortic stenosis: The U.K. TAVI (United Kingdom transcatheter aortic valve implantation) registry. J Am Coll Cardiol [Internet]. 2011;58(20):2130‐2138. 10.1016/j.jacc.2011.08.050 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

