Loss of TSC1/TSC2 sensitizes immune checkpoint blockade in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 35119931
- PMCID: PMC8816329
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abi9533
Loss of TSC1/TSC2 sensitizes immune checkpoint blockade in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
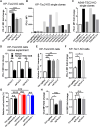
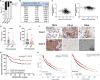
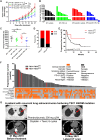
Tuberous sclerosis complex subunit 1 (TSC1) and 2 (TSC2) are frequently mutated in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), however, their effects on antitumor immunity remained unexplored. A CRISPR screening in murine KrasG12D/Trp53-/- (KP) model identified Tsc1 and Tsc2 as potent regulators of programmed cell death ligand 1 (Pd-l1) expression in vitro and sensitivity to anti-programmed cell death receptor 1 (PD-1) treatment in vivo. TSC1 or TSC2 knockout (KO) promoted the transcriptional and membrane expression of PD-L1 in cell lines. TSC2-deficient tumors manifested an inflamed microenvironment in patient samples and The Cancer Genome Atlas dataset. In syngeneic murine models, KP-Tsc2-KO tumors showed notable response to anti-PD-1 antibody treatment, but Tsc2-wild-type tumors did not. Patients with TSC1/TSC2-mutant NSCLC receiving immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) had increased durable clinical benefit and survival. Collectively, TSC1/TSC2 loss defines a distinct subtype of NSCLC characterized as inflamed tumor microenvironment and superior sensitivity to ICB.
Figures


References
-
- Rizvi H., Sanchez-Vega F., la K., Chatila W., Jonsson P., Halpenny D., Plodkowski A., Long N., Sauter J. L., Rekhtman N., Hollmann T., Schalper K. A., Gainor J. F., Shen R., Ni A., Arbour K. C., Merghoub T., Wolchok J., Snyder A., Chaft J. E., Kris M. G., Rudin C. M., Socci N. D., Berger M. F., Taylor B. S., Zehir A., Solit D. B., Arcila M. E., Ladanyi M., Riely G. J., Schultz N., Hellmann M. D., Molecular determinants of response to anti-programmed cell death (PD)-1 and anti-programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) blockade in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer profiled with targeted next-generation sequencing. J. Clin. Oncol. 36, 633–641 (2018). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huang Q., Zhang H., Hai J., Socinski M. A., Lim E., Chen H., Stebbing J., Impact of PD-L1 expression, driver mutations and clinical characteristics on survival after anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy versus chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis of randomized trials. Onco. Targets. Ther. 7, e1396403 (2018). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Coelho M. A., de Carné Trécesson S., Rana S., Zecchin D., Moore C., Molina-Arcas M., East P., Spencer-Dene B., Nye E., Barnouin K., Snijders A. P., Lai W. S., Blackshear P. J., Downward J., Oncogenic RAS signaling promotes tumor immunoresistance by stabilizing PD-L1 mRNA. Immunity 47, 1083–1099.e6 (2017). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akbay E. A., Koyama S., Carretero J., Altabef A., Tchaicha J. H., Christensen C. L., Mikse O. R., Cherniack A. D., Beauchamp E. M., Pugh T. J., Wilkerson M. D., Fecci P. E., Butaney M., Reibel J. B., Soucheray M., Cohoon T. J., Janne P. A., Meyerson M., Hayes D. N., Shapiro G. I., Shimamura T., Sholl L. M., Rodig S. J., Freeman G. J., Hammerman P. S., Dranoff G., Wong K. K., Activation of the PD-1 pathway contributes to immune escape in EGFR-driven lung tumors. Cancer Discov. 3, 1355–1363 (2013). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

