Age-related DNA methylation on Y chromosome and their associations with total mortality among Chinese males
- PMID: 35120273
- PMCID: PMC8920452
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.13563
Age-related DNA methylation on Y chromosome and their associations with total mortality among Chinese males
Abstract
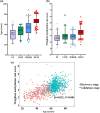
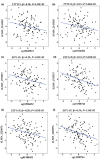
In view of the sex differences in aging-related diseases, sex chromosomes may play a critical role during aging process. This study aimed to identify age-related DNA methylation changes on Y chromosome (ChrY). A two-stage study design was conducted in this study. The discovery stage contained 419 Chinese males, including 205 from the Wuhan-Zhuhai cohort panel, 107 from the coke oven workers panel, and 107 from the Shiyan panel. The validation stage contained 587 Chinese males from the Dongfeng-Tongji sub-cohort. We used the Illumina HumanMethylation BeadChip to determine genome-wide DNA methylation in peripheral blood of the study participants. The associations between age and methylation levels of ChrY CpGs were investigated by using linear regression models with adjustment for potential confounders. Further, associations of age-related ChrY CpGs with all-cause mortality were tested in the validation stage. We identified the significant associations of 41 ChrY CpGs with age at false discovery rate (FDR) <0.05 in the discovery stage, and 18 of them were validated in the validation stage (p < 0.05). Meta-analysis of both stages confirmed the robust positive associations of 14 CpGs and negative associations of 4 CpGs with age (FDR<0.05). Among them, cg03441493 and cg17816615 were significantly associated with all-cause mortality risk [HR(95% CI) = 1.37 (1.04, 1.79) and 0.70 (0.54, 0.93), respectively]. Our results highlighted the importance of ChrY CpGs on male aging.
Keywords: DNA methylation; Y chromosome; aging; mortality.
© 2022 The Authors. Aging Cell published by Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Age-dependent DNA methylation patterns on the Y chromosome in elderly males.Aging Cell. 2020 Feb;19(2):e12907. doi: 10.1111/acel.12907. Epub 2019 Feb 21. Aging Cell. 2020. PMID: 30793472 Free PMC article.
-
Ageing-associated changes in DNA methylation in X and Y chromosomes.Epigenetics Chromatin. 2021 Jul 2;14(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13072-021-00407-6. Epigenetics Chromatin. 2021. PMID: 34215292 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation and risk of cardiovascular disease in a Chinese population.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021 May 12;21(1):240. doi: 10.1186/s12872-021-02001-w. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021. PMID: 33980183 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylome profiling of all-cause mortality in comparison with age-associated methylation patterns.Clin Epigenetics. 2019 Feb 8;11(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13148-019-0622-4. Clin Epigenetics. 2019. PMID: 30736859 Free PMC article.
-
A methylation panel of 10 CpGs for accurate age inference via stepwise conditional epigenome-wide association study.Int J Legal Med. 2025 May;139(3):1193-1203. doi: 10.1007/s00414-024-03365-2. Epub 2024 Dec 5. Int J Legal Med. 2025. PMID: 39633164
Cited by
-
Risk prediction model of frailty and its associated factors in older adults: a cross-sectional study in Anhui Province, China.Front Nutr. 2025 Jul 17;12:1611914. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1611914. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40747332 Free PMC article.
-
G-quadruplex DNA and RNA in cellular senescence.Front Aging. 2024 Oct 9;5:1491389. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2024.1491389. eCollection 2024. Front Aging. 2024. PMID: 39444378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translating genetic findings to epigenetics: identifying the mechanisms associated with aging after high-radiation exposure on earth and in space.Front Public Health. 2024 Mar 22;12:1333222. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1333222. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38584916 Free PMC article.
-
Sex as a biological variable in ageing: insights and perspectives on the molecular and cellular hallmarks.Open Biol. 2024 Oct;14(10):240177. doi: 10.1098/rsob.240177. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Open Biol. 2024. PMID: 39471841 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen, Y. A. , Lemire, M. , Choufani, S. , Butcher, D. T. , Grafodatskaya, D. , Zanke, B. W. , Gallinger, S. , Hudson, T. J. , & Weksberg, R. (2013). Discovery of cross‐reactive probes and polymorphic CpGs in the Illumina Infinium HumanMethylation450 microarray. Epigenetics, 8(2), 203–209. 10.4161/epi.23470 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheng, C. , Wang, Q. , Zhu, M. , Liu, K. , & Zhang, Z. (2019). Integrated analysis reveals potential long non‐coding RNA biomarkers and their potential biological functions for disease free survival in gastric cancer patients. Cancer Cell International, 19, 123. 10.1186/s12935-019-0846-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

