Therapeutic options for premature ovarian insufficiency: an updated review
- PMID: 35120535
- PMCID: PMC8815154
- DOI: 10.1186/s12958-022-00892-8
Therapeutic options for premature ovarian insufficiency: an updated review
Erratum in
-
Correction: Therapeutic options for premature ovarian insufficiency: an updated review.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2023 Sep 4;21(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s12958-023-01133-2. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 37667342 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
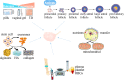
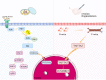
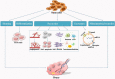
Primary ovarian insufficiency (POI) is a rare gynecological condition. This disease causes menstrual disturbances, infertility, and various health problems. Historically, hormone replacement therapy is the first-line treatment for this disorder. Women diagnosed with POI are left with limited therapeutic options. In order to remedy this situation, a new generation of therapeutic approaches, such as in vitro activation, mitochondrial activation technique, stem cell and exosomes therapy, biomaterials strategies, and platelet-rich plasma intra-ovarian infusion, is being developed. However, these emerging therapies are yet in the experimental stage and require precise design components to accelerate their conversion into clinical treatments. Thus, each medical practitioner bears responsibility for selecting suitable therapies for individual patients. In this article, we provide a timely analysis of the therapeutic strategies that are available for POI patients and discuss the prospects of POI therapy.
Keywords: In vitro activation; Mitochondrial activation technique; Platelet rich plasma; Premature ovarian insufficiency; Stem cell therapy; Therapeutic options.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Beck-Peccoz P, Persani L. Premature ovarian failure. Orphanet J rare dis [internet]. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2006; [cited 2020 Aug 8];1:9. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16722528. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nippita TA, Baber RJ. Premature ovarian failure: A review. Climacteric. Climacteric; 2007;10:11–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

